Newsletter blog
Children categories
Let’s Declare a Climate Emergency in Hornsby
Hornsby Shire Climate Action has set up an online petition calling on Hornsby Council to declare a climate emergency. Declaring a climate emergency is a vital step in building support for the very large changes required to restore a safe climate.
Once declared, the council must enforce policies that will reduce emissions as much as possible. They must also educate the public about the state of emergency. Click here to sign the petition.
Good News for Streamwatch
From July the management of the Streamwatch program was taken over by the Greater Sydney Landcare Network. This is a great relief. As previously reported there was a risk that this valuable program would be discontinued because NSW government annual funding of a measly $100,000 was uncertain. Streamwatch, with almost 300 volunteers, plus 30 years of data has to have a paid coordinator.
Data will be migrated to the SEED platform – an open government repository of environmental information hosted by the environmental cluster within the Department of Planning, Industry and Environment. The Landcare Network is delaying taking on new volunteers until the new testing system is finalised.
This is a great citizen science project that has given school, children community groups and individuals a meaningful way of getting out into the environment.
Now the Cumberland State Forest is Under Threat
NSW Forestry Corp has lodged a proposal to sell off parts of the Cumberland State Forest for housing subdivision. More critically endangered forest would be cleared. Not just Mirvac but now NSW Forestry Corp want to decimate some of these forests in West Pennant Hills.
Documents have been lodged with the Hills Council applying for the rezoning of two areas that would then be the subdivided for low density housing. They claim the land is surplus to their needs but what about the needs of the people of Sydney to keep existing green space?
An on-site meeting was held with Greens MP David Shoebridge on 11 August.
For updates on the campaign go to www.facebook.com/pg/ForestinDanger.
Mirvac Development a Threat to Critically Endangered Ecological Communities
The Office of Environment and Heritage has alerted the Hills Council to the fact that the presence of Blue Gum High Forest and Sydney Turpentine Ironbark Forest, both critically endangered ecological communities are listed as potential ecological communities that meet the principles and criteria for serious and irreversible impact as defined under the Biodiversity Conservation Act. Under this act development consent cannot be granted to proposals that impact on serious and irreversible impact entities.
The Office of Environment and Heritage and an independent ecologist have identified large areas of Blue Gum High Forest within the proposed development footprint and the bushfire asset protection zones.
The Forest in Danger group does not believe that the planning proposal 1/2018/PLP can be approved in its current format. The draft development control plan, the planning proposal and the voluntary planning agreement would have to be re-exhibited.
For more details see previous issue of STEP Matters or the Forest in Danger Facebook page.
Update on the Bayview Golf Course Development
Good news! The Land and Environment Court has upheld the decision by the Northern Beaches Council and Sydney North Planning Panel to refuse the seniors housing development application on part of the Bayview Golf Course land. The site compatibility certificate had been granted by the Department of Planning to allow a development, but the council still had to approve the details of the development approval. Council knocked back the application on the grounds that its size was excessive and its impact on local biodiversity.
The developer wanted to amend the site compatibility certificate so that the council would not have grounds for refusal. The site compatibility certificate has now expired. The developer will have to start from scratch if they want to try again.
Byles Creek Valley should be Protected
Hornsby Council is undertaking a four-month review at a cost of $70,000 into potential rezoning and acquisition of land in Byles Creek Valley that is currently unprotected. Council has come to this conclusion in all reviews and reports in the past.
In 2014 Hornsby Council made a very comprehensive submission to the NSW government pushing for acquisition of Byles Creek Valley land in 2014. In this document council’s expert environmental team stated that:
The Byles Creek catchment has been identified as environmentally significant due to the unique environmental values of the area … The preservation of these lands provides connectivity between the significant vegetation corridor along Byles Creek and Lane Cove National Park. The connectivity of this corridor ensures the ability for species to disperse between reserves and the national park and for the transferral of genetic material. The conservation value of this corridor is further emphasised by its inclusion as a core area in the NSW Biodiversity Investment Opportunities Map as part of the NSW government’s Green Corridors Program.
The valley is noted for the high quality of the water in the Creek that flows into the Lane Cove River. It is used as a reference standard for water quality in the shire.
As a member of the Powerful Owl Coalition, STEP strongly supports the protection of the valley as it links with breeding habitat for the Powerful Owl.
Our thanks to the Byles Creek Valley Union for this information.
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park Plan of Management
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park is one of the most popular national parks in NSW, with over 3 million visits each year. The existing plan of management for the park was written in 2002. Since that time there has been a steady increase in visitors coming to the park, new recreational uses have become popular, information about the values of the park has improved and new approaches to managing fire and pests and weeds have been developed. The NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) is preparing a new plan of management for the park and island nature reserves.
As part of preparing the new plan of management NPWS has released five discussion papers exploring some of the key management themes that will be included in the new plan:
- aboriginal cultural values
- natural, visitor experience and shared heritage values
- recreational activities
- visitor destinations
- leases licences and consent
NPWS is keen to hear what the community has to say about future management of the park.
Comments close on 15 September 2019. Click here to contribute your ideas and comment.
There will be other opportunities to provide input to the plan of management when the draft plan is exhibited for public comment.
Friends of Lane Cove National Park Celebrate 25 Years
On 25 May the Friends of Lane Cove National Park put on a special celebration. They were founded in 1994 after major bushfires burnt out large areas of the park and exposed the bushland to weed invasion. They have been working for 25 years to restore the bushland of Lane Cove National Park together with the NPWS staff.
The occasion was also the official opening of Jenkins Kitchen after its restoration using a NSW government Heritage Near Me grant and resources from the Friends, their time and money, to restore the interior and set up displays of historical and wildlife items. The building built in 1855 is believed to be the oldest in Ku-ring-gai.
NSW Government News
Since the re-election of the Berejiklian government there has been a mixed bag of news in relation to the environment. Here are some brief points.
New Environment Minister
We welcome the appointment of Hornsby MP Matt Kean as Minister for Energy and Environment. He has made promising statements emphasising the importance of national parks and the need for new action on climate change and threatened species. However his power over the short-sighted members of cabinet is uncertain.
Changes to the Office of Environment and Heritage
The Office of Environment and Heritage is no longer a separate entity - it now comes under the Department of Planning, Industry and Environment. The level of influence that staff from the former Office of Environment and Heritage will have in the future is uncertain.
More National Park Funding Cuts
The abolition of the Office of Environment and Heritage makes it difficult to assess the level of funding for national parks under the budget relative to previous years. The ABC has reported that, in the latest budget, $80 million is being cut from NPWS.
In a statement to the ABC, the government said those cuts would come through more efficient work practices in the department. How can the department be made more efficient after the $121 million cut in the 2016–17 budget that lead to about 100 ranger positions being lost? We believe there is more restructuring of front-line staff to come.
Local Green Spaces Funding
The budget included $9 million to improve open space in Frenchs Forest with new green connections, walking tracks and bike paths linking the local community to nearby bushland corridors. This is a development to watch out for. Will there be more mountain bike tracks?
Land Clearing
The Audit Office released its assessment of the administration of the land clearing laws in June. The media release included this statement:
The processes supporting the regulatory framework are weak and there is no evidence-based assurance that clearing of native vegetation is carried out in accordance with approvals.
Maps of vegetation that landowners need to operate under the new legislation are still not available.
It was announced recently that the government will not be pursuing prosecutions of landowners who have cleared land illegally under the Native Vegetation Act that applied prior to the Biodiversity Conservation Act in 2018. This new act provides for a lot more self-assessment so the past clearing may have been legal under the new law.
Data show massive increases in land clearing over recent years. The data are often disputed on the basis that some clearing is of woody weeds or regrowth. Is that a reasonable excuse? There is no big picture data to help determine whether the regrowth should be encouraged, not cleared.
There are also severe concerns with the renewed Regional Forestry Agreements and the attitude to logging in native forests, particularly koala habitat. Detail about these issues is covered by the Nature Conservation Council.
No matter what data are revealed the area of native vegetation needs to be increased significantly, not decreased, to halt the trend of land degradation and species extinction.
Feral Horses in Kosciuszko National Park
A statewide campaign to protect Kosciuszko National Park from destructive feral horses has forced the government to debate its controversial Wild Horse Heritage Act. This will occur on 22 August.
Meanwhile the number of horses is increasing and the damage to the fragile mountain ecology worsens as the government has suspended the removal program.
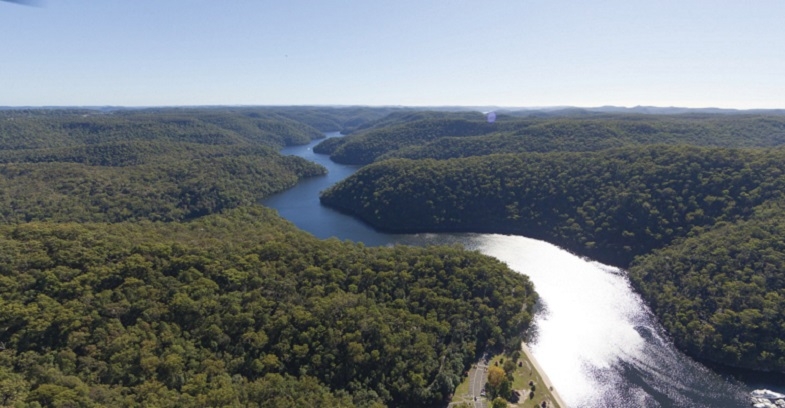
Raising Warragamba Dam Wall
The proposal to raise the Warragamba Dam wall by 14 m may have hit a couple of stumbling blocks:
- a UNESCO world heritage committee says that the proposal could threaten the listing of the Blue Mountains as a World Heritage area
- modelling of the reduction in flood risk shows the higher wall will have very little benefit
The government is currently preparing an environmental impact statement. Some of the work so far was leaked. It revealed that about 1,300 ha of the world heritage area would be permanently damaged including significant aboriginal cultural sites. The UNESCO committee has asked the government to consult with them before making the final decision. Federal government approval is also required because of the world heritage listing.
It has been stated that the objective of the proposal is to reduce the impact of flooding of the Hawkesbury-Nepean floodplain by holding back water after heavy rainfall for longer. However some of the charts from modelling the effects of the wall raising prepared for the EIS were leaked to the Sydney Morning Herald.
As Figure 1 shows there is very little change in the water outflows during a likely flood event.
In the case of a major flood such as the 1867 flood that is the highest recorded, the picture is similar. This level is believed to be equivalent to a one-in-500 year event (see Figure 2).
The reason for the small reduction in flooding is that there are major rivers that flow into the Hawkesbury-Nepean system below Warragamba Dam such as the Nepean, Grose and Colo. This compounded by the flow downstream being held back at a number of pinch points where the river valley narrows.
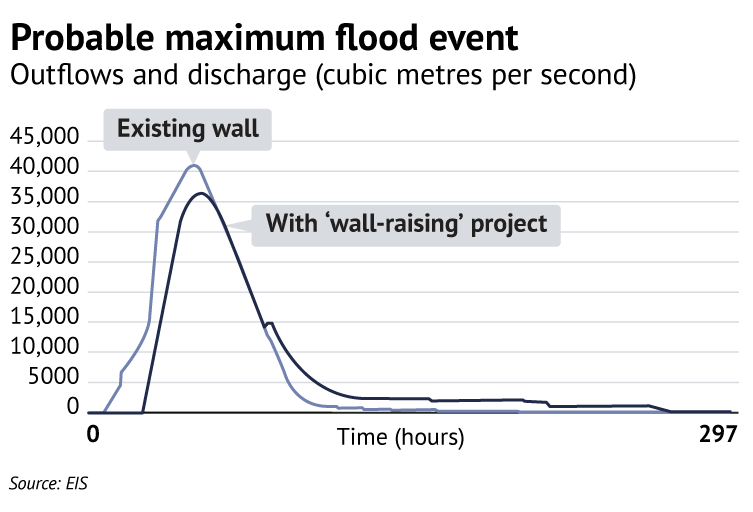
Figure 1
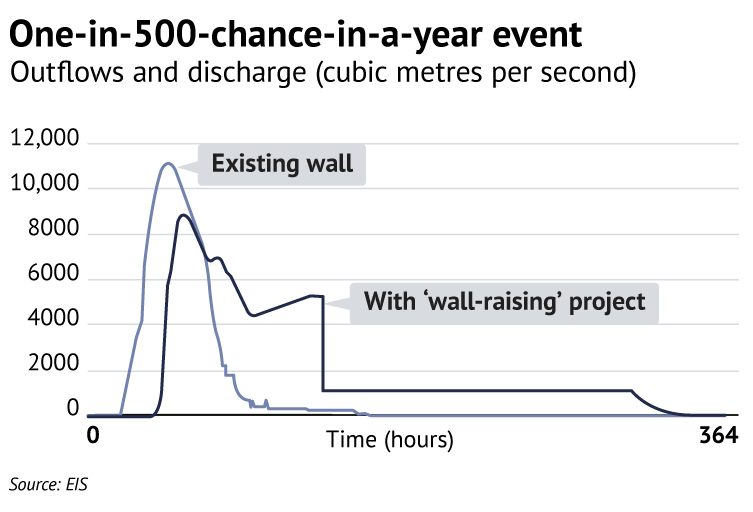
Figure 2
The River Red Gum is an Icon of the Driest Continent
River red gums, Eucalyptus camaldulensis, are among the most iconic of Australia’s eucalypts. They are the most widely distributed of all the eucalypts. They grow along rivers, creeks, waterways and flood plains where many Australians like to picnic, so most of us get to know and love them.
Formerly known as Eucalyptus rostrata, the species was one of the first eucalypts encountered in parts of Australia by European settlers. Curiously, the name camaldulensis comes from the Italian monastery of Camaldoli near Naples, where a specimen grown from seed in a private garden was given the name Eucalyptus camaldulensis in 1832. No one knows how the seed got to be there!
River red gums can be very large spreading trees with huge trunks more than 5 m around. In parts of Australia, such as along the Murray River, they can be very erect trees reaching more than 45 m tall.
Most specimens have smooth bark with a mottling of multiple colours ranging from creams to orange and red, but there may be a skirt of fibrous grey bark for the first few metres of the base. They are called river red gums because they grow along rivers and their wood when freshly exposed is a bright red; almost blood-coloured.
River red gums have been used by Indigenous people for canoes, bowls, shields, and other utensils. The wood is red is because it contains very high levels of chemicals such as polyphenols, which are a natural antibiotic when combined with air.
These chemicals not only protect the living tree from disease and some pest attacks, but make the timber very durable. These chemicals meant river red gums were used for medicinal purposes by Indigenous people. The wood has been widely used for railway sleepers, fence posts, and piers and wharfs where durability and water resistance are desirable. They have been widely planted overseas and in some countries pose a serious weed problem.
The trees can have very long lives, and may reach 1,000 years of age. They grow very rapidly when conditions are favourable and so become large trees quite quickly. But as they get older it is very difficult to age them without damaging the tree and putting it at risk of disease and decay. So their ages are estimated, as no one wants to be responsible for killing a grand old tree just to confirm its age!
Older specimens almost always develop large hollows, which can take centuries to form. The hollows provide refuges for birds, mammals and reptiles. The nesting sites are often raucously defended by brightly coloured parrots. The trees and the nectar from their small white flowers are also very important for honey production – a large tree in full flower over the warmer months can attract so many bees that the whole tree can be heard humming from many metres away; it’s a wonder the tree doesn’t take off.
At certain times of the year, often during summer, river reds can be very heavily grazed by insects to the point where their leaves are skeletonised. The trees look as though they are about to die, but they are very resilient and a few months later most are back to a full and healthy canopy. Another insect, the psyllid, also feeds on and skeletonises the leaves. It has a sweet, waxy covering called a lerp that protects the vulnerable insect nymphs beneath. Some Indigenous groups scrape off the lerps, roll them into a ball, and eat them like a lolly.
Surviving Floods and Driving Rain
Any tree that can live for a millennium must be adaptable, so like some other eucalypt species, river red gums can shed up to two-thirds of their foliage when soils dry out during a drought, which reduces water demand and prevents the trees from wilting. This shedding often causes people to complain about the trees when they grow in towns and cities, but when the rains come a few months later they rapidly produce new leaves and are soon once again in full canopy.
River red gums can tolerate immersion in flood waters for up to nine months. They do this by having extensive roots, some of which contain a spongy, air-filled tissue called aerenchyma that allows for the accumulation and transport of much-needed oxygen in waterlogged soils. This adaptation to stressed soils also means river red gums can do quite well in disturbed urban soils when the urban sprawl impinges on their natural domain.
River red gums readily seed after flooding events and great numbers of young trees may germinate. However, relatively few survive to maturity due to competition from other red gums, other trees, and weeds. They may also struggle to survive in some places due to a lack of water.
Because river reds occur in some of the driest and harshest parts of the Australian mainland, you might think they are very efficient users of water. However, nothing could be further from the truth. The trees can have very deep, spreading and searching root systems, which tap into subterranean water, even if the water is many metres from the trunk. They are luxury water users with very little capacity for water use control. If water becomes really limiting, they simply wilt.
Territorial Trees
E. camaldulensis produces a water-soluble chemical that is washed from its leaves by rain. These chemicals inhibit the growth of other plants, including river red gum seedlings, under the canopy. This phenomenon is called allelopathy, and along with a dense canopy inhibits plant growth under the trees. These chemicals are washed from the soil by flood water, which makes way for the germination of seedlings after floods. This is a wonderful mechanism that ensures seedlings do not germinate when conditions are dry and where they would compete with the parent tree for limited water, but germination is facilitated when there is plenty of water and soils are wet.
Some people think river red gums are dangerous because they shed large limbs without warning on calm, still, summer days. There is no doubt this does happen, but there is no clear evidence they shed limbs more often than other species.
The problem is complex, because they tend to grow everywhere people want to go. They provide shade along waterways on a hot, dry continent. In going to places where the trees grow, people tend to compact the soil with their vehicles and footpaths, which can be causes of limb shedding. The compaction of the soil affects soil moisture and aeration, which can lead to limb shedding.
In other contexts such as farms where limbs are shed, many old river red gums are growing in highly disturbed or changed ecosystems. Furthermore, many of these remnant specimens are often stressed and getting older and so more prone to shedding.
River red gums trace the watercourses of mainland Australia, and are easily seen from aeroplanes as you cross the continent. They connect the continental fringes with its arid heart. Their lives can span many human generations and it is nice to think that the majestic old trees that pull at our heartstrings have done the same to previous generations and, if we and they are lucky, will continue to do so for generations of Australians yet to come.
This article appeared in The Conversation on 12 July. It is written by Gregory Moore, Doctor of Botany at Melbourne University.
Here’s some more information about the importance of river red gum in maintaining healthy landscapes and controlling salinity:
Stands of river red gum are associated with the surface flooding regime of watercourses and related ground water flow. The species is a profligate and opportunistic water user, and this is a contributing factor to the maintenance of water tables at depth. Even without large amounts of empirical data it is clear that loss of large tracts of the species in the Murray River corridor would have a major impact on the hydrology of the system, as well as on vegetation communities and associated biodiversity.
Which Urban Trees can Survive a Changing Climate?
There is lots of research demonstrating the benefits of trees in urban areas. Not only do they camouflage the grey asphalt and concrete of roads and footpaths, they can reduce temperatures and the need for air conditioning in buildings. They also improve the microclimate by retaining moisture in the air and soil and they encourage residents to get out into the community and enjoy beautiful shaded areas.
Tree planting is an effective and efficient way to adapt to climate change. However as climate change leads to higher temperatures and more variable and lower rainfall we need to consider how the popular trees used in urban areas will respond to the changes.
Different species have different levels of tolerance of heat, lack of water and other threats posed by climate change.
Research teams from Macquarie University (including former STEP president Prof Michelle Leishman) and Western Sydney University, have embarked on a project called Which Plant Where. The project is supported by Hort Innovation Australia, the Department of Planning, Industry and Environment and the Australian government. Their mission is to find the best plant species for urban landscapes that will be resilient to climate change.
The project works with the nursery industry to gather evidence on species’ resilience to extreme heat and drought by testing plants to their limits in research glasshouses. This work will inform plant growers and nurseries on how to adapt their business, by identifying the new challenges posed by climate change, as well as selecting diverse ranges of climate-ready species. They advise landscape architects, designers and urban planners about not only the best planting choices, but also how to increase the biodiversity of our cities.
We need to know how our current tree canopy will be affected as well as plan new plantings.
The research team recently published a study (Burley et al) that investigated likely climate change impacts on 176 of the most common tree species planted across Australian cities. The analysis showed more than 70% of these species will experience harsher climatic conditions across Australian cities by 2070.
Some of the most commonly planted trees are unlikely to survive. Conversely, in some cooler climate areas, such as Orange, the number of suitable species may increase. These impacts will progressively worsen as climate change intensifies. A proactive approach is needed to identify new climate-ready species and plantings. Tree species growing in warmer cities are more likely to be affected than those in cooler cities. Some species, such as the golden wattle (Acacia longifolia) or the prickly paperbark (Melaleuca styphelioides) might not make it in northern cities unless we invest precious resources – such as water – to maintain these civic assets. Other species, such as the native frangipani (Hymenosporum flavum) or the tuckeroo (Cupaniopsis anacardioides) will likely become more suitable for planting in southern cities.
Australian cities are blessed with a higher diversity of tree species compared to other cities globally. However, the 30 most commonly planted species make up more than half of Australia’s urban forests. This poses a great risk for our cities. If we were to lose one or two of these common species, the impact on our urban tree cover would be immense. Trees are a long-term investment that will be affected by the very factors that they are meant to mitigate. Consequently, our best insurance is to increase the diversity of our trees.
The study highlights the need for more research:
- which species experience a reduction in growth or, even mortality, during extreme weather events and the duration of any growth reduction
- variation of impacts in different climate zones, for example subtropical areas are likely to experience greater declines in growth than temperate areas
- whether it is feasible with some species to mitigate impacts by providing more irrigation, selective pruning or planting in a more sheltered position
- investigate new choices of species suitable for the urban environment from the huge range of Australian native species
The NSW government announced a plan in February to plant five million trees in Greater Sydney by 2030. They are counting trees planted in streets, parks, backyards, neighbourhoods and schools with an objective of increasing the tree canopy from 16.8% to 40%. Councils can apply for grants for tree planting projects. Individuals can register the trees they plant.
Reference
Hugh Burley, Linda J. Beaumont, Alessandro Ossola, John B. Baumgartner, Rachael Gallagher, Shawn Laffan, Manuel Esperon-Rodriguez, Anthony Manea, Michelle R. Leishman (2019) Substantial declines in urban tree habitat predicted under climate change, Science of the Total Environment 685, 451–462
Australia’s Possible Future in 40 Years Time
CSIRO Futures released a report in June on Australia’s future in the next 40 years, called Australian National Outlook 2019 (ANO 2019).
The report is the outcome of a collaborative project that took two years involving more than 50 leaders from over 20 organisations across industry, non-profit and university sectors, including the National Australia Bank, Shell, Australian Red Cross, Monash University, the Grattan Institute and the Wentworth Group of Concerned Scientists. ANO 2019 uses CSIRO’s integrated modelling framework to project economic, environmental and social outcomes to 2060 under two scenarios in the context of responses to six identified future challenges. The challenges are:
- risks and opportunities from the rise of Asia
- technology development and implementation skills
- climate change and environmental degradation – our response and that of the rest of the world
- population aging
- trust in government and business
- social cohesion
The report concludes that if we resist the changes needed to meet the challenges, essentially business as usual, the outcome is described as the Slow Decline. The alternative scenario of bold action is called Outlook Vision.
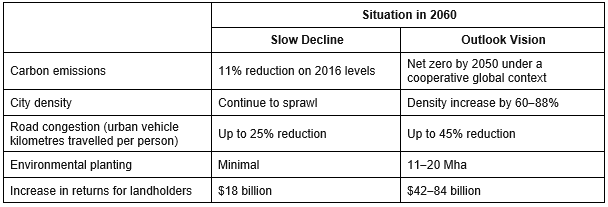
In brief some of the environmental outcomes of the two scenarios are summarised in Table 1.
Here is some context to the projections in the assumptions that have been made.
Population Growth
The report had to model a lot of information but the major factor has been taken as a given. They have assumed that population growth will continue on the current high path. Population will be 41 million by 2060 with Sydney and Melbourne growing to 8 or 9 million people and Brisbane and Perth growing to 4 or 5 million. That is an extra 16 million people in 40 years. Our population in 1980 was about 14.5 million. So by comparison the increase in the past 40 years was about 11 million. CSIRO expects this growth to be accommodated within our finite land and ecosystems.
It is very sad that no mainstream organisation is willing to publicly countenance a reduction in population growth and demonstrate the implications this will have for our future.
Water Supply
Very little detail is provided about the costs of maintaining an adequate urban water supply for the burgeoning population. It seems the assumption is made that sufficient desalination can be installed. The cost of this is incorporated in the infrastructure costs of catering for the growth in population.
Climate Change Scenarios
This is what they say about the implications of climate change under the two scenarios (from https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2018EF000922).
The most reliable estimates aligned to the scenarios indicate that 4°C global warming without adaptation could lead to a global per annum GDP loss of 7.2% and an Australian per annum GDP loss of 1.6% by 2100. If mitigation can limit the global warming to 2°C by 2100, the global per annum GDP loss would be reduced to 0.5–1.6% by 2050–60 and to 1.8% by 2100, and the Australian per annum GDP loss would be reduced to 0.6% by 2100. The GDP loss would be further reduced by adaptation.
There is a lot of detail in the modelling of the implications of climate change in the two scenarios. The quotation above gives a scale to the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Table 1
Land Use and Biodiversity
Taking into account climate change and the need to maintain agricultural exports and feed our own population very radical change is envisaged under the Outlook Vision scenario. There is a strong message about the necessity to end the trend of rural land degradation and to restore ecosystems. Productivity improvements through plant genomics and digital agricultural mapping technology will not be enough. The statements about ecosystem health are significant in the context of the current federal and state governments’ attitudes towards exploiting the environment. Here are a few quotes from the report:
… the high agricultural productivity rates necessary for the Outlook Vision outcomes will not be possible without sustaining broader ecosystem health, particularly in the face of effects associated with a changing climate.
… agriculture not only affects the environment but is also highly dependent on the quality of natural assets and the ecosystem services they provide for its productivity and profitability.
Soil Health
The report highlights the negative trajectory of soil health that has resulted from intensive agriculture on fragile soils. Several aspects of current soil health will limit productivity, particularly long-term erosion, acidification, low carbon levels, soil compaction and soil nutrient decline. The risk of erosion increases with an increasing frequency of droughts and lower groundcover. Ecosystem and land management practices must turn around the deterioration of soil health.
Agriculture is also dependant on access to a reliable supply of clean water, pollination services and shade and shelter provided through native vegetation. Land degradation needs to be halted and, where possible, remediated to ensure the long-term viability of agriculture.
New forms of investment that provide financial support for carbon farming are recommended as a means of providing a return to landowners for the benefits of improving ecosystem services.
Emissions Reduction through Carbon Sequestration
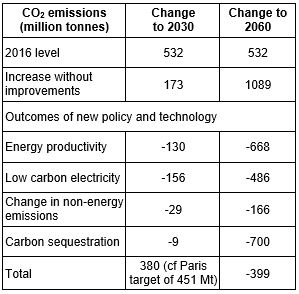
Under Outlook Vision carbon sequestration will play an essential part. By 2060, up to 30 million hectares – or roughly half of Australia’s marginal land within more intensively farmed areas – could be profitably transitioned to carbon plantings, which would increase returns to landholders and offset emissions from other sectors. The success of this scenario depends on increases in productivity so that less land is needed to produce the required food. Table 2 shows the potential sources of change from the current annual emissions of greenhouse gases of 532 million tonnes under the Outlook Vision scenario.
Table 2
In theory there could be an excess of carbon sequestration that could be sold on the international carbon market. However it would be more prudent to keep this stored carbon as a buffer against bushfire and other risks.
Out of the 30 million hectares 11–20 Mha is defined as environmental plantings rather than direct carbon forestry (i.e. native–endemic mixed environmental plantings that provide the most suitable habitat for biodiversity). This will build resilience against future climate change. This translates to between 12 and 24% of intensive agricultural land (or between 32 and 42% of the total land area used for carbon forestry). The overall transition of land use is shown in Figure 1.
The wide range of returns to landowners of $42 to 84 billion in Table 1 is indicative of the complex interplay between the impacts of climate on modelled agricultural production and tree growth, among other factors. The modelling results show that additional income from other land use change can more than offset any reductions in agricultural production due, in part, to the fact that agricultural production will be concentrated on more productive land, with less productive land transitioned to other uses. However the returns to landowners are affected by carbon prices that will be dependent of the level of global cooperation in reducing emissions.
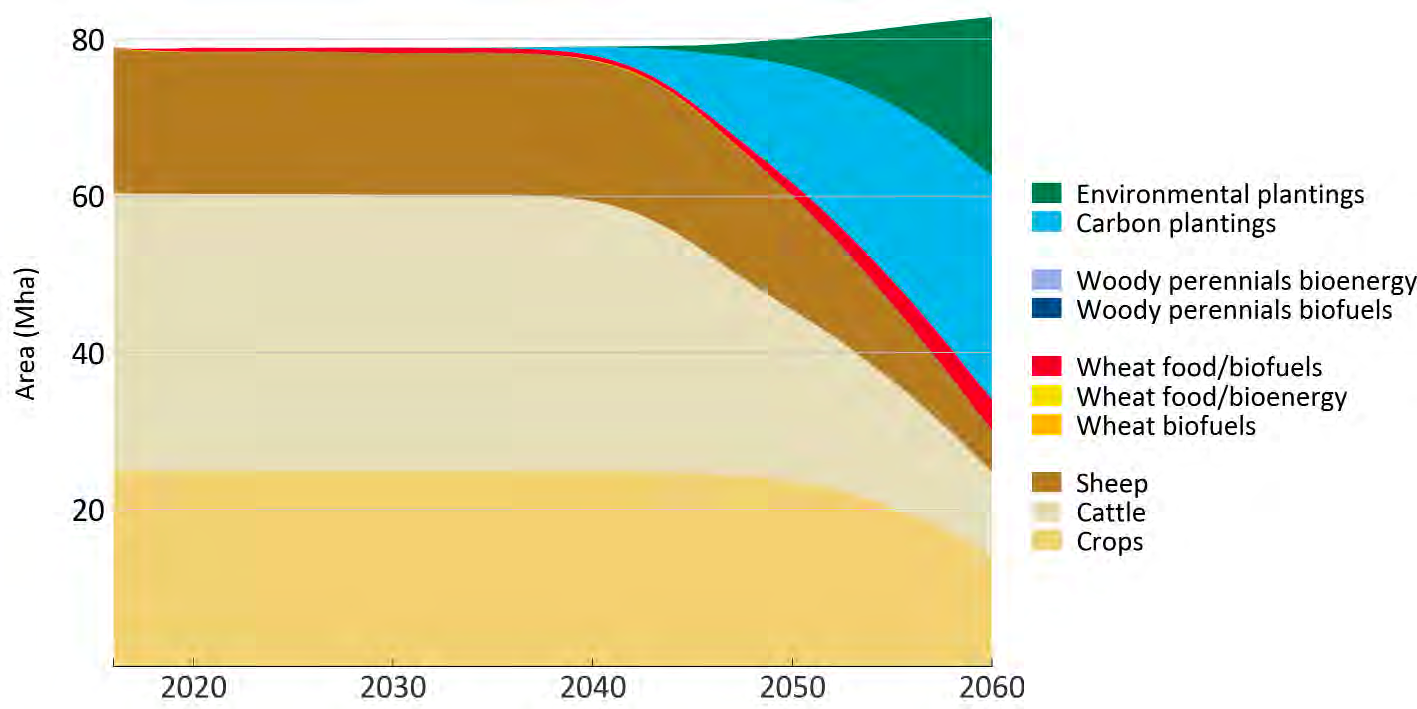
Carbon and environmental plantings on this scale are a significant land use shift, and so require careful planning, consultation and engagement with the community, particularly regional communities. Such considerations will include protecting prime agricultural land for food and fibre production and avoiding adverse effects on water supplies.
Conclusion
CSIRO has produced several of these big picture reports before:
- Future Dilemmas: Options to 2050 for Australia's Population, Technology, Resources and Environment in 2002
- Balancing Act: A Triple Bottom Line Analysis of the Australian Economy in 2005
Where are they now?
The Morrison government has been re-elected despite having a very limited set of policies for change. We need a government with a long-term vision and a willingness to explain convincingly the reasons for change. We should be able to reach a consensus despite there being some losers as well as winners.
Buy a Bundle of Books and Save
This is a great opportunity to do some Christmas shopping. We have decided to reduce the price of our books if they are purchased in a bundle.
Postage costs about $11 but it is free to pick up from South Turramurra.
Contact This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. for more information.
Book bundle 1 = $25 ($17.50 for members)
- Field Guide to the Bushland of the Lane Cove Valley +
- Sydney's Natural World +
- Understanding the Weather
This is a saving of $45 (or $31.50 for members)!
Book bundle 2 = $80 ($56 for members)
- Book bundle 1 +
- Rocks and Trees
This is a saving of $50 (or $35 for members)!
2040 – Join the Regeneration
STEP is supporting the screening of the film 2040 at Roseville Cinema. Booking is essential. We need a minimum of 68 bookings before the screening can go ahead. Your payment will be refunded if this number is not reached.
The previous screening organised by Ku-ring-gai Council in July was booked out.
2040 is a hybrid feature documentary that looks to the future, but is vitally important NOW! Award-winning director Damon Gameau (That Sugar Film) embarks on journey to explore what the future could look like by the year 2040 if we simply embraced the best solutions already available to us to improve our planet and shifted them rapidly into the mainstream.
Structured as a visual letter to his 4-year-old daughter, Damon blends traditional documentary with dramatised sequences and high-end visual effects to create a vision board of how these solutions could regenerate the world for future generations.
Citizen Science Project - Dead Tree Detective
Western Sydney University and the University of New England have set up a Citizen Science Project called the Dead Tree Detective.
The aim of the project is to collect observations of dead or dying trees around Australia. It sounds a bit grim, but knowing where and when trees have died will help us to work out what the cause is, identify trees that are vulnerable, and take steps to protect them.
This project will allow people Australia-wide to report observations of tree death. In the past, there have been many occurrences of large-scale tree death that were initially identified by concerned members of the public such as farmers, bushwalkers, bird watchers and landholders. Collecting these observations is an important way to monitor the health of trees and ecosystems.
All you need is a smart phone with a camera and GPS. It is also possible to report on paper by asking for a survey form by emailing This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
The leader of the project, Prof Belinda Medlyn wants to get better data about how trees respond to drought.
How our native plants cope with these changes will affect (among other things) biodiversity, water supplies, fire risk and carbon storage. Unfortunately, how climate change is likely to affect Australian vegetation is a complex problem, and one we don’t yet have a good handle on.
Threatened Species Children’s Art Competition
STEP has supported the Threatened Species Children’s Art Competition since 2017. The competition has been a great success and has now expanded to Victoria, and other states are expressing interest.
Administration has now been taken over by the Humane Society International – the largest worldwide charity caring for animals.
Children choose a threatened native species, then create a drawing or painting of it with an accompanying short explanation of their work. Entries close on 2 August 2019.
Seventy NSW finalists will be chosen for a two-week exhibition in Sydney, with winners announced at Parliament House Sydney on 6 September 2019.
Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest Declared Critically Endangered
The NSW Threatened Species Scientific Committee, established under the Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016, has made a Final Determination to list Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest (STIF) in the Sydney Basin Bioregion as a critically endangered ecological community. This classification already applies under the federal Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act.
The highest threat category is now applied because STIF has experienced large:
- reductions in geographic distribution
- degrees of environmental degradation
- disruptions of biotic processes and interactions
There is an estimated 2,940 ha of STIF remaining, or less than 10% of the estimated original distribution.
Remnants of STIF are poorly represented in the formal reserve network, and unreserved areas are subject to the threat of vegetation clearing. The total area under reservation is estimated to be 570 ha, equivalent to less than 2% of the estimated pre-1750 distribution or 20% of the remaining extent.
Remnants of STIF have historically been subjected to a range of anthropogenic disturbances including logging, grazing by domesticated livestock and burning at varying intensities.
Remnants are typically small and fragmented and are susceptible to continuing attrition through clearing for routine land management practices due to the majority of remnants being located in close proximity to rural land or urban interfaces.
Applications to the NSW Land and Environment Court demonstrate that there is ongoing pressure to clear STIF in the course of developing private properties or for the establishment of asset protection zones.
STIF is subject to ongoing invasion by an extensive range of naturalised plant species. Weed invasion is exacerbated by the proximity of remnants to areas of rural and urban development and the associated influx of both weed propagules from gardens and nutrients contained in stormwater runoff, dumped garden waste and animal droppings.
John Martyn Research Grant Award for 2019
We are very pleased to announce that the John Martyn Research Grant for 2019 has been awarded to Gabriella Hoban. Gabriella’s research project is entitled Soil Characteristics as Indicators of Restoration Trajectories in Urban Woodlands. This subject is highly relevant to STEPs aims to restore degraded ecological communities.
She has provided us with this description of her project.
Hi! I’m Gabby. I am an honours student at the University of New South Wales. I love ecology, ecological restoration and conservation and have a slight obsession with plants.
For my honours project I will be studying the effect of soil characteristics on restoration trajectories in urban woodlands. My research will be based in western Sydney within the Cumberland Plain Woodland, a critically endangered vegetation community. In this region, a concentration of threatened species and ecological communities overlap with intense development pressure.
Through my project I aim to quantify the relationship between the abundance of exotic and native plant species in relation to soil constituents in bushland reserves with agricultural land use legacies. Soil samples will be collected and the effect of soil properties on restoration trajectories will be determined.
My research will build on existing data from long-term study sites established in 1989. This research provides an exciting opportunity to examine long term trends in regenerating bushland.
I hope this research can inform conservation efforts not only at this site, but also similar grassy reserves recovering from legacies of former agricultural land use that span a large area across south-eastern Australia.
Thank you to STEP and its members for the opportunity.
Last Attempt to Stop the Mirvac Development Plans for the IBM Site
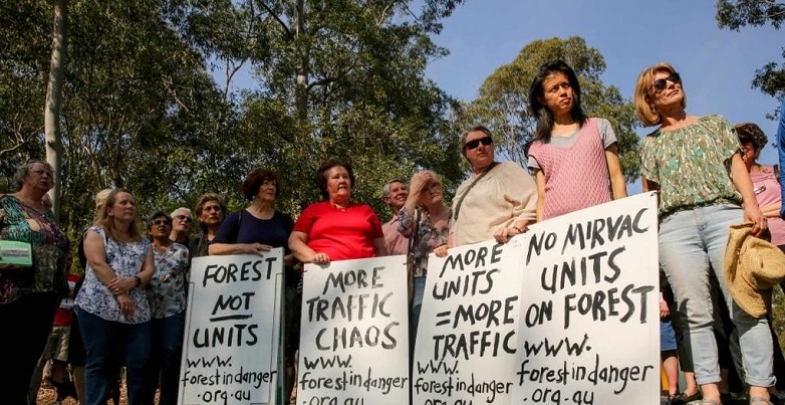
The final deadline was set at 31 May for submissions on the Hills Council’s applications to the NSW government to change the zonings in their local environment plan and insert some special provisions in the development control plan. These changes will facilitate development on the land owned by Mirvac that currently contains the old IBM corporate headquarters on the corner of Coonara Road and Castle Hill Road in West Pennant Hills next to the Cumberland State Forest.
The basic framework of the proposals is unchanged from earlier plans described in STEP Matters (Issue 198). The main purpose of the council application at this stage is to facilitate the development of 600 dwellings. Ancillary aspects are that, if the housing development proceeds, Mirvac will sign a voluntary agreement to allow the existing playing field on the land to become public open space and pay for the development of a soccer field with synthetic turf and the necessary public access road.
The design of the housing development will be subject to further scrutiny at the development application stage but if these current plans are approved, the basic framework will be set in concrete (lots of it!).
Even though part of the site is currently developed as a corporate park, these buildings are surrounded by mature tree plantings. The majority of the site is classified as Blue Gum High Forest or Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest, both critically endangered. This is a unique opportunity to preserve one of the few remaining areas of high quality vegetation and its associated fauna habitat in north-western Sydney. Its proximity to Cumberland State Forest adds to the value of this preservation through its connectivity and boosting of resilience of the vegetation.
Hence STEP is opposed to the whole development proposal.
Future of the forested area
The future management of the large forested area that is to be zoned E2 (environmental conservation) which contains critically endangered ecological communities and fauna, is completely unknown. The development control plan amendment relating to the site refers to the residents as being responsible for the cost of maintenance of the 'significant vegetation'. This is totally unrealistic.
It is essential that a stewardship or conservation agreement be established defining responsibilities and funding of management together with a vegetation management plan. This should be in place before any dwellings are occupied.
As the E2 land will be for the benefit of the whole local community, not just the residents of the Mirvac developments, it is appropriate that the Hills Council be responsible for its management.
Synthetic playing field
The proposal for the synthetic playing field should not go ahead until the environmental impact of the use of this surface is thoroughly assessed. A detailed analysis is required of the impact on the bushland below the field of:
- stormwater runoff from the hard surface
- runoff of degraded synthetic grass and substrate pieces
- the loss of soil biota under the artificial surface
- the risk from a fire in the surrounding bushland spreading to the field
- conversely, the surface itself is mostly made of rubber and will be much hotter than in the surrounding vegetated areas, so what impact will this have on the bushland and wildlife?
Of course no floodlighting should be allowed so close to bushland that is home to several nocturnal species such as the Powerful Owl and several species of bats.
Development plans
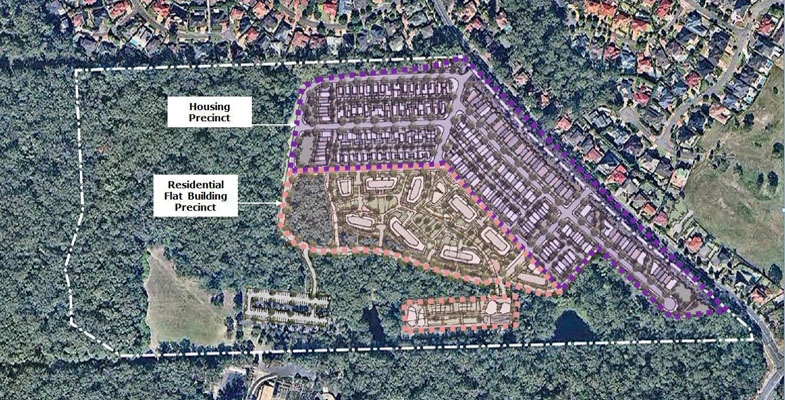
The image at the top of the page shows the proposed layout of the development. The medium density housing area (200 dwellings) is along the edges of the site while the high density zone (flats up to six stories) is lower down next to the forested areas.
The main argument from Mirvac in favour of the development is its proximity to the new Cherrybrook Metro Station. Residents will however have to walk up a steep hill and cross Castle Hill Road to get to the station. The shortest possible walk is 800 m. The other side of Castle Hill Road which is in the Hornsby Council area is currently zoned low-density residential that will no doubt be planned for higher density development in the future as the station is now operating.
Overdevelopment
The major reason for objections to the proposals is the level of development. The residents of West Pennant Hills have rallied strongly against the proposals. Over 4,000 objections have been received by the Hills Council. They are concerned about the increase in traffic on already congested roads as well as the environmental impact of the development.
The main point is that the existing IBM corporate park is a valuable asset. The buildings should not be knocked down. With a bit of imagination alternative uses could be found that will not lead to destruction of the mature native vegetation that surrounds the buildings and the car park.
In any case the council and Mirvac have not demonstrated that there is a need for this huge housing area. We note that the Department of Planning document Cherrybrook Structure Plan: Vision for Cherrybrook Station Surrounds (September 2013) does not envisage any residential development on the site. Increases in housing are planned for neighbouring areas north and further west of Castle Hill Road with a total number of new dwellings planned of 3,200 by 2036.
The plan is an example of the notorious spot re-zonings that have plagued development in Sydney. A developer comes up with a plan that is outside the planning guidelines. The local council knocks it back so the developer is able to go directly to the Department of Planning to gain approval via the Gateway Process. The new planning minister, Rob Stokes, has stated that this system will not continue but we will have to see how that can come about.
As Hornsby Council says in their submission:
Any decision for this site should be deferred until a precinct-wide structure plan or strategy is adopted for all the land parcels surrounding the Cherrybrook Metro Station.
...
The proposal by Mirvac to redevelop the subject property for residential purposes is likely to trigger further owner/developer-led spot rezoning applications in the area. This would lead to an ad hoc approach to land use planning for the Metro Station precinct. The process would undermine the planning framework for both councils and lead to poor outcomes for the Cherrybrook community.
Housing plan is overdeveloped
The documents indicating the layout of the medium-density housing precinct show houses that are crammed together, some on blocks as small as 86 m2 that are only 4 m wide. Even with some of the wider lots most of the street will be taken up by driveway access.
There will be little space for street trees. The front and back yards will also be too small for trees to grow with a beneficial canopy.
The design of the subdivision needs to take account of the need for liveability of streets in the face of current heat in summer and expected increases with climate change.
There are also several other concerns about the details of the development and how it will impact on the surrounding forest. These relate to clearing of riparian zones and impingement of asset protection zones into the E2 area and Cumberland State Forest.
We have covered several of these concerns in previous comments on this proposal. They are very concerning but basically STEP is opposed to the development in its entirety.
Conclusion
Mirvac’s website reveals the company’s Biodiversity Policy. The policy states:
At Mirvac, we aim to be an overall positive contributor to environmental sustainability. We firmly believe that responsibly managing our biodiversity impacts will enable us to strategically assess biodiversity-related risks and opportunities and anticipate and respond proactively to emerging regulations and societal expectations.
Mirvac’s plans for the IBM site are clearly not compatible with their Biodiversity Policy.
Let’s Introduce Vehicle Fuel Efficiency Standards and Save Money Too
The transport sector is Australia’s second fastest growing source of carbon dioxide emissions and yet we still don’t have any standards which apply to new vehicle fuel efficiency.
Road transport contributed 16% to total CO2 emissions in 2000 and this grew to 18% in 2010 and 21% in 2016.
We are the only OECD country with no minimum fuel standard while more than 80% of the global vehicle market has adopted fuel standards. We have had standards for many years relating to other vehicle emissions such as nitrous oxides, carbon monoxide and particulates.
Standards in other countries
The EU applied mandatory standards from 2009 requiring a light vehicle fleet average of 130 g CO2/km by 2015 and 95 g/km by 2020–21.
These standards have been further developed requiring a reduction by 15% by 2025 and 37.5% by 2030 relative to 2020–21. Standards will also be applied to heavy vehicles.
The USA has had voluntary standards since 1975 that have not been effective. In 2012 standards were introduced including a reduction by 3% each year after 2012 applied to each manufacturer. They are enforced with the potential of the loss of licence to sell vehicles. The effective standard is slightly higher than applies to the EU. However President Trump is now threatening to loosen the standards.
Testing methods are problematic
The sources used for this article comment on ongoing issues with the testing methods being used to monitor vehicle fuel use.
The standard methods used in Europe were developed in the 1970s. They are called the New European Drive Cycle (NEDC) and they have been found to be unrealistic because they assume that the car is being driven at a constant speed with mild acceleration. Actual consumption that has been tested in real conditions show the gap is getting worse and is now believed to be about 40%.
The sources don’t explain why the gap is getting worse apart from the legal methods of manipulating the tests, e.g. by using low-resistance tyres. The latest EU standards will require cars to have on-board monitoring systems in future.
Clearly there is a need for proper testing of on-road vehicle emissions. One wonders about the accuracy of the greenhouse gas reporting for Australia’s transport emissions. The same applies to reporting by other countries.
The standards are applied on a fleet wide basis but then manufacturers have to apply the standard to their individual range of vehicles. The projection of future emission levels requires an estimate of the nature of the vehicle fleet that is a combination of several cohorts of ages of vehicles plus the average distances travelled by each type of vehicle.
Australia’s experience
The current situation is that in 2017 Australia’s light passenger average CO2 emissions were 172 g/km compared with 118.5 g/km in the EU. In the case of light commercial vehicles Australia’s average was 222 g/km compared with 164 g/km in the EU.
In addition to the lack of efficiency standards, according to a report from Transport Energy/ Emissions Research [1] several other factors contribute to Australia’s higher vehicle emissions:
- Use of heavier and greater engine capacity cars such as SUVs (even in comparison with the USA). It is reported that in 2017 the average fuel use in Australia was 20% higher than in the USA. This trend is getting worse.
- Use of automatic transmissions that are reported to be less fuel efficient.
- Greater distances travelled. The Australian Bureau of Statistics reported that total travel by passenger vehicles in Australia was 142 billion kilometres in 2000. This has been growing to 176 billion kilometres in 2016, an increase of 24%.
- The most fuel efficient model choices in Australia are not as efficient as in Europe leading to the suggestion that manufacturers are taking advantage of our lack of mandatory standards.
- Our vehicle fleet is older than in other countries and turnover is slower so it takes longer for the benefit of newer, more fuel-efficient vehicles to flow through to the fleet as a whole. Conversely driving a vehicle for a longer period could produce lower emissions when allowance is also made for the emissions during manufacture.
It is also suggested that Australians are paying paying about 30% more for fuel than they should (provided better fuel efficiency doesn’t encourage more driving).
Australia’s attempts to introduce standards
Australia has had voluntary efficiency standards since 1978 that were equivalent to 195 g CO2/km (2000) and 161 g CO2/km (2010) but these have not been achieved.
In 2010, the ALP government decided that mandatory CO2 emissions standards would apply to new light vehicles from 2015, i.e. a national fleet wide average of 190 g/km in 2015 and 155 g/km in 2024. However, the change in government in 2013 meant the standards would not see the light of day.
Several reports have been written analysing the options for introducing standards.
The Climate Change Authority produced a report in December 2016 that proposed that the first phase of mandatory standards be introduced with effect from 2018, by which time local manufacture of automobiles was expected to have ceased.
The standards would progressively reduce CO2 emissions from new light vehicles to 105 g/km in 2025, almost half the then current level of 192 g/km. This 2025 standard would broadly bring Australia into line with the USA and still trail the tighter EU targets by several years.
A Ministerial Regulation Impact Statement found that the introduction of a standard of 105 g/km phased in over 2020–25 would cost $16.2 billion compared with no standards but would lead to:
- national fuel savings of $27.5 billion
- reduce greenhouse gas emission by 65 Mt by 2030
- create an overall net benefit to the economy of $13.9 billion
This calculation allowed for a cost of carbon emissions of about $50/tonne.
The Automotive Association has lobbied against the proposal on the grounds that cars will be more expensive. Implementation of a standard to reduce CO2 emissions to 105 g/km is estimated to increase the average cost of a new car in 2025 by about $1500. This, however, would be offset several times by fuel savings of about $8500 over the life of the vehicle, leaving motorists better off.
How about electric vehicles?
The rollout of electric vehicles in Australia is being held back by their cost and lack of recharging stations. Labor’s election proposal to require that 50% of new passenger vehicles sold be electric vehicles by 2030 was hysterically dismissed by Scott Morrison. He claimed the policy would make life impossible for tradies as the ute would be uneconomic and it would spell the end of the weekend trip away in the SUV.
Of course this was all nonsense as the cost of electric vehicles is coming down rapidly and is expected to be similar to internal combustion engines by 2025. We might even revive the local manufacturing industry? In any case perhaps it would be a good idea to hire a large SUV for a weekend trip rather than driving these large vehicles around to drop the kids off at school or commute to work.
One question about the use of electric vehicles is the carbon emissions if they are being recharged using electricity from the current high use of coal-fired generation. The data I have found indicates that electricity consumption to run an electric vehicle could be 6–10 Kw h per 100 km. Currently Australia’s emissions from electricity generation is 800 g/Kw h. So that equates to carbon emissions from electric vehicles of 48–80 g/km.
Conclusion
The available evidence suggests that legislative action regarding vehicle CO2 emissions is long overdue. The federal government must take action to ensure total CO2 emissions from road transport are reduced by introducing emission standards and by taking several additional measures such as increasing public transport and reducing distances driven.
Introducing these new regulations quickly is a priority because it takes years for them to actually work their way through the market to the new vehicle fleet.
References
[1] Transport Energy/Emission Research Pty Ltd Vehicle CO2 Emissions Legislation in Australia – A Brief History in an International Context
Threat to a Common European Tree
The costly problem of ash dieback has been highlighted in New Scientist.
This fungal disease caused by Hymenoscyphus fraxineus was first detected in Britain in 2012 having crept across Europe from the east. Its origin is Asia and it affects the common ash Fraxinus excelsior. It's predicted to destroy more than 90% of the many million ash trees, killing saplings within a year of infection. Coming on top of Dutch elm disease and various infections of both English oak species, it's a concern in a country that has, through millennia, lost most of its native forests.
They are all Fiddling while the World Burns
 When the USA became serious about WWII they brought about an amazing mobilisation of their entrepreneurial industrial potential. That is surely the way in which the fight against global warming will be conducted when we eventually wake up to the urgency. In the meantime most of the world’s leaders and most of the populace seems content enough to drift along ignoring that elephant in the room.
When the USA became serious about WWII they brought about an amazing mobilisation of their entrepreneurial industrial potential. That is surely the way in which the fight against global warming will be conducted when we eventually wake up to the urgency. In the meantime most of the world’s leaders and most of the populace seems content enough to drift along ignoring that elephant in the room.
Part of that mobilisation will surely be the recognition that population growth is a major cause of ongoing warming. Halve the population and we roughly halve much of the pollution causing warming as well as other pollution such as plastics.
That brings us to what’s happening in Australia.
With an average of about 12.5 million people over the past 220 years we have degraded our major river systems, caused a terrible list of plant and animal extinctions, degraded our topsoils and more and are now busily overpopulating our major cities - with consequent physical and social consequences.
Our current annual rate of population growth of 1.7% will lead to doubling every 42.5 years. That means 50 million in 2061, 100 million in 2104 and 200 million in 2146 and so on.
You would think that those numbers would be enough to promote some discussion of where we are heading and where we want to head and how to go about it. But no, the Coalition, Labor and the Greens, along with our major environmental groups such as the ACF and NCC, all seem intent on ignoring the elephant and ensuring further degradation and destruction of the Australian natural world.
Why is this thus? We think there are a few reasons.
Firstly there is huge ignorance around the maths of exponential growth. It’s amazing to find so many educated, even scientifically educated, people who have not a clue about the consequences of 1.7% growth.
Secondly, the mainstream media and political world has insisted in conflating population growth with protecting the borders and racism. You talk about less population and so many assume that you are dog-whistling and really mean that we don’t want those refugees. The ABC has a terrible record in this regard.
Thirdly, the big end of town, those whose lobbyists haunt the corridors of our parliaments, cheque books in hand, has convinced many that without economic growth we shall all become destitute. That is simply self-serving rubbish that suits their economic interests. More people mean more housing, more furnishings, and more of most things. It’s not the environment they worry about – it’s their never-ending need for more economic activity and more profit.
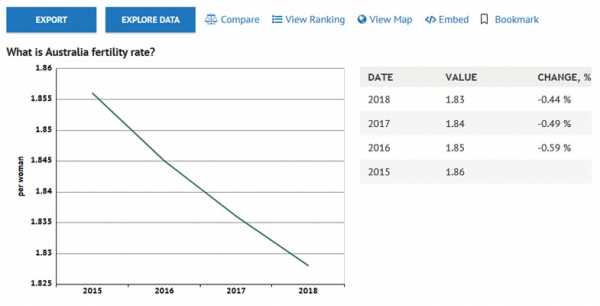
Australia’s fertility is now about 1.83 which will eventually produce a declining population because it is below the replacement level of 2.1. In addition, some 50,000 people leave Australia permanently every year. This means that we can accept 70,000 immigrants per year and eventually stabilise our population. We should do so. There is plenty of room there for refugees.
STEP has never dog-whistled!
It’s hard, however, to know how we shall ever start to manage the situation so long as none of the elites are prepared to discuss it and so long as the environmental organisations don’t have the guts to confront it.
We have been writing about population for over thirty years and much more detail can be gleaned from our Position Paper on Population.
By John Burke, former president of STEP and chief author of STEP’s Position Paper on Population, has written this update on the population issue.
The Future of Tasmanian Leatherwood
Visiting Tasmania at leatherwood flowering time in February was a nice experience apart from the weather. It has a perfumed flower likened to a four-petalled version of the five-petalled English wild dogrose. Tasmanian Leatherwood Eucryphia lucida, of honey fame, is a high rainfall, temperate rainforest species often found close to rivers (see the two pictures below taken at Pencil Pine Creek, Cradle Mountain). Driving along the Lyell Highway from Queenstown to Derwent Bridge we saw several beehive ‘mini cities’ in valleys, clearly exploiting the setting of the plant.
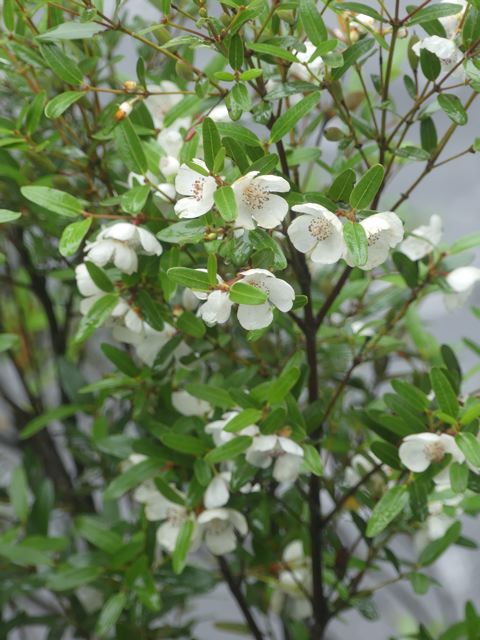
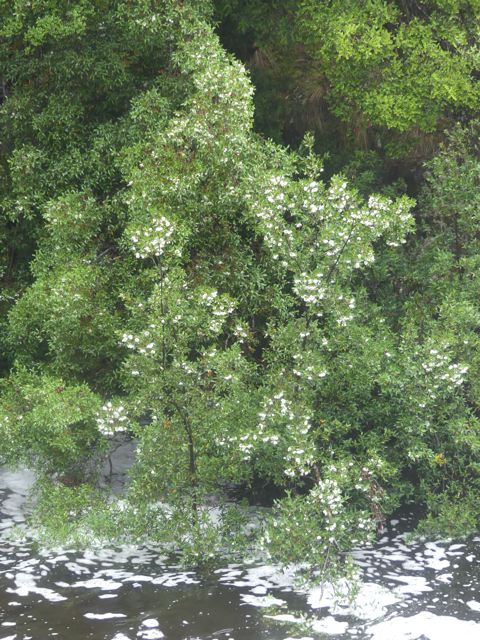


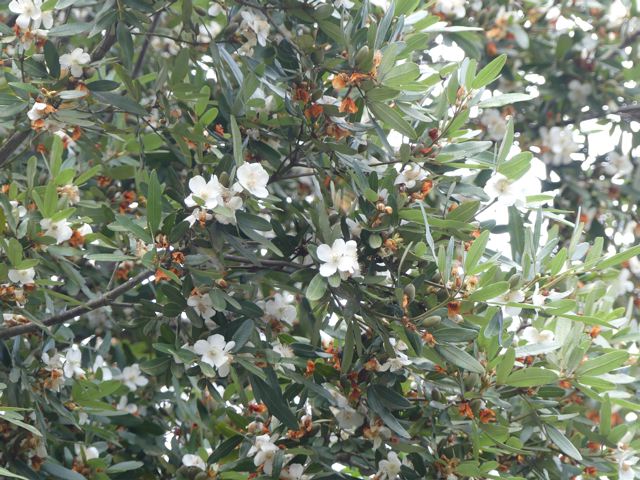
Australia has five species of Eucryphia, one of the commoner ones, E. moorei (see the picture at the top of the page and below) liking wet highland environments from the Illawarra to north-east Victoria.
The easiest place to see it locally in late summer is across the road from the Robertson Pie Shop where a windbreak hedge of small trees to 5 metres follows a fence line. We also saw it in flower at Fitzroy Falls, several specimens being scattered through the rainforest apron of the valley, though you wouldn't spot them without their flowers.
 The latter setting is more typical for the tree and it seems to also like rocky sites – we located another tiny colony in Hawkesbury Sandstone on rocky Bundanoon Creek in Meryla State Forest south of Moss Vale.
The latter setting is more typical for the tree and it seems to also like rocky sites – we located another tiny colony in Hawkesbury Sandstone on rocky Bundanoon Creek in Meryla State Forest south of Moss Vale.
All Australian species grow in high rainfall, cool to warm temperate settings ranging from E. moorei of the Illawarra to E. wilkiei of the mountain cloud forests of North Queensland. But globally the picture of Eucryphia is bigger.
There are a further two species, E. cordifolia and E. glutinosa, from cool temperate rainforests of South America. And it turns out that there are striking similarities in the flavour of honeys from the Chilean E. glutinosa, known there as Ulmo, and that of Tasmanian Leatherwood. This is particularly extraordinary since the two continents severed their link via Antarctica more than 60 million years ago.
Eucryphia species have been cultivated in Australia, Europe and elsewhere, and include pink-flowered forms and hybrids. While the variety of rugged and inaccessible settings of common species like E. moorei may mean they are fairly safe, the northern species, E. jinksii and E. wilkiei are both local and endemic to their settings and are listed as threatened. E. wilkiei of Mt Bartle Frere cloud forests is especially vulnerable to climate change – horrendous heat records were set there this summer.
Of further concern, Tasmania was beset by wildfires this summer, particularly in the Huon Valley region south-west of Hobart. This, and the drought that amplified it, had a variety of negative effects on Leatherwood. There were multiple tree losses and flowering was weak: trees that did flower produced very little nectar. The suspected link to climate change is a cause for concern and Leatherwood may yet be another canary in the coal mine. Anyway, if you're looking to buy Leatherwood honey this year it won't easy or cheap.
References
Wikipedia
Blog: The Nature of Robertson
By John Martyn
How did the IPBES Assessment come up with the Figure of a Million Species at Risk of Extinction?
In May 2019 the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) published its global assessment of the state of the earth’s biodiversity and its prospects for change up to 2050. This is the first such report since the landmark Millennium Ecosystem Assessment published in 2005. The IPBES Assessment is the outcome of negotiations by 134 governments using data provided by 500 biodiversity experts from over 50 countries.
The aim of the IPBES Assessment is explained by its chair, Sir Robert Watson:
The loss of species, ecosystems and genetic diversity is already a global and generational threat to human well-being. Protecting the invaluable contributions of nature to people will be the defining challenge of decades to come. Policies, efforts and actions – at every level – will only succeed, however, when based on the best knowledge and evidence. This is what the IPBES Global Assessment provides.
It examines causes of biodiversity and ecosystem change, the implications for people, policy options and likely future pathways over the next three decades if current trends continue, and other scenarios.
My question is how did IPBES work out the number of species existing and at risk of extinction?
How many species are there?
Several different approaches have been used to estimate the actual total number of species on earth. Frankly it is impossible to know the number with any reasonable level of precision. The various methods give a very wide range of answers – from 3 million to over 100 million. Most of the more recent estimates based on thoughtful approaches are in range of 5 to 20 million.
The main point is to understand the relative level of extinction that could take place. We are finding new species all the time. There are frequent reports of excursions into rainforest finding lots of new beetles or other insect species. New species are even being found in our local area, viz Julian’s Hibbertia.
The report uses the results of a study published in 2011 [1]. The study uses data of past records showing how the knowledge of the number of phyla, classes, families, genii and species for each taxa have increased over time. For each level of the description hierarchy (phyla, class, etc) if fewer and fewer new types are being found then it is assumed that we are getting close to finding the final actual number. The method fits a regression line to the asymptotic graph of the known number over time to estimate the point where the line would reach the limit of increases. Then the phyla build into the number of classes and so on.
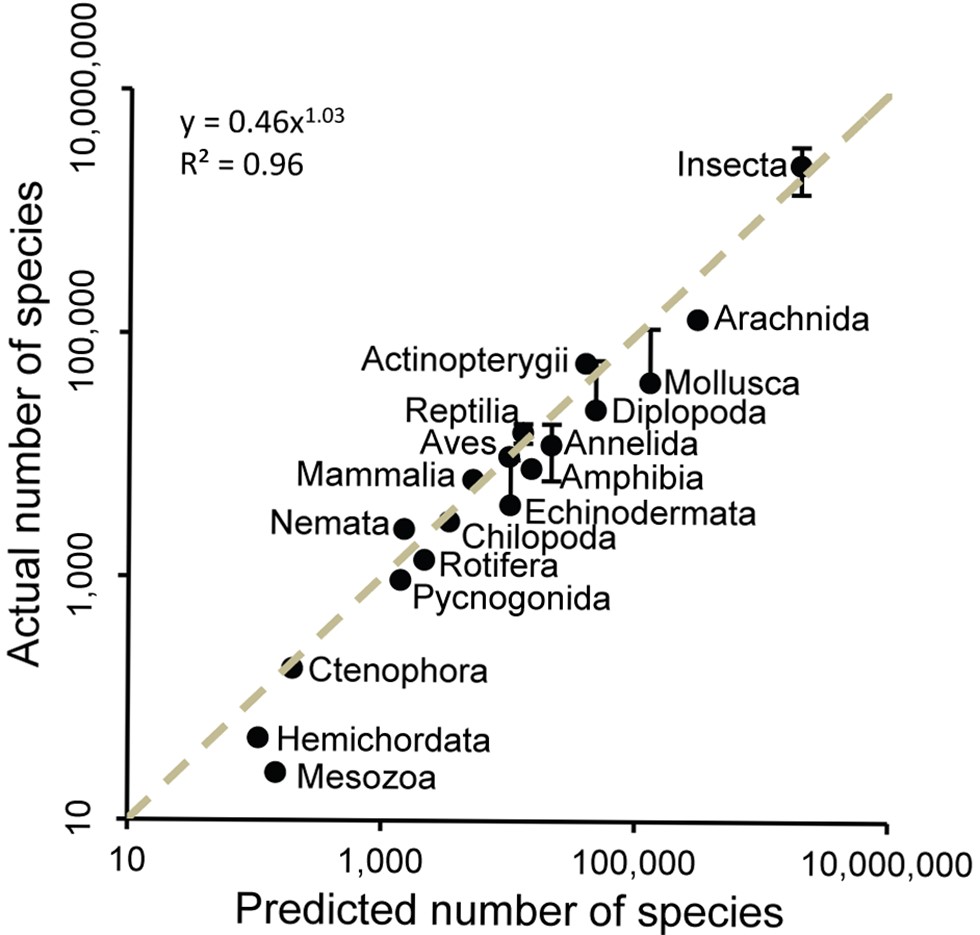 One argument in favour of this method is that species that are yet to be identified are living in small numbers or in niche areas so they are of less significance in terms of total life on the planet.
One argument in favour of this method is that species that are yet to be identified are living in small numbers or in niche areas so they are of less significance in terms of total life on the planet.
This approach was validated against well-known taxa such as mammals. When applied to all eukaryote kingdoms the approach predicted:
- ∼7.77 million species of animals
- ∼298,000 species of plants
- ∼611,000 species of fungi
- ∼36,400 species of protozoa
- ∼27,500 species of chromists
In total the approach predicted that ∼8.74 million species of eukaryotes exist on earth. Restricting this approach to marine taxa resulted in a prediction of 2.21 million eukaryote species in the world's oceans.
In spite of 250 years of taxonomic classification and over 1.2 million species already catalogued in a central database, the study’s results suggest that some 86% of existing species on earth and 91% of species in the ocean still await description.
How did IPBES derive the million at risk figure?
Species are defined as being at risk of extinction if their numbers are declining to the extent that the population may no longer be viable. They may not become totally extinct for a long time. For example, plants may live for many years but may not be reproducing.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species’ definitions of vulnerable, endangered and critically endangered are used to encompass the overall concept of being at risk of extinction.
The IUCN Red List is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of plant and animal species. It uses a set of quantitative criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species. These criteria are relevant to most species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognised as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity.
Currently the IUCN Red List status is that 36% of the 47,677 species assessed are threatened with extinction, which represents:
- 21% of mammals
- 30% of amphibians
- 12% of birds
- 28% of reptiles
- 37% of freshwater fishes
- 70% of plants
- 35% of invertebrates
that have been assessed.
Averaged across all the taxonomic groups of animals and plants that have had IUCN Red List assessments, about 25% of species are threatened. But the sparse data for insects so far suggest it might be lower – estimates range from 10 to 15% – so IPBES used a figure of 10% that might turn out to be conservative. If insects are three-quarters of animal and plant species, there are 5.5 million of them, of which 10% are threatened (so, more than half a million insect species are threatened). If 25% of the other 2.6 million species are threatened, that’s more than half a million non-insect species threatened. Hence the rounded total figure is about 1 million species at risk of extinction.
Are the headlines about loss of species meaningful?
Some very broad assumptions have been used in coming up with the figure of 1 million species at risk of extinction over the next few decades. One wonders if this is a meaningful exercise.
Are people going to take more notice of this announcement?
Is there a better way of illustrating the significance of the threat of massive biodiversity loss over the next few decades?
Maybe the percentages quoted earlier mean more, such as 70% of plants and 21% of mammals?
Another factor that may be more significant is the loss of biomass of plants and animals. Recent studies have pointed to the significant decline in biomass of insects. Dr Sanchez-Bayo from Sydney University pointed this out in a recent paper to the journal Biological Conservation [2].
Besides all the important functions that insects play in our ecosystems - such as pollination, or recycling nutrients - they are also an essential element in the food chain that supports life on our planet. When the insects go, the frogs, birds and mammals don't have food.
The IPBES Assessment is mostly devoted to describing the reasons for species decline and what should be done about it. The reasons are not hard to find: exploitation, land clearing, weed and pathogen invasion, climate change.
Currently biodiversity law and policy is inadequate to redress the situation. If we are to halt the continued loss of nature, then the world’s legal, institutional and economic systems must be reformed entirely. And this change needs to happen immediately.
Reference
[1] Mora, C; Tittensor, DP; Adl, S; Simpson, AGB; Worm, B (2011) How Many Species are there on Earth and in the Ocean? PLOS Biol 9(8): e1001127
[2] Sánchez-Bayo, F and Wyckhuys, KAG (2019) Worldwide Decline of the Entomofauna: A Review of its Drivers. Biological Conservation 232, 8–27
Great Season for Fungi
Our walk in Fox Valley on 14 April revealed some surprises. A Powerful Owl was spotted and there were several unusual examples of fungi as identified by John Martyn.
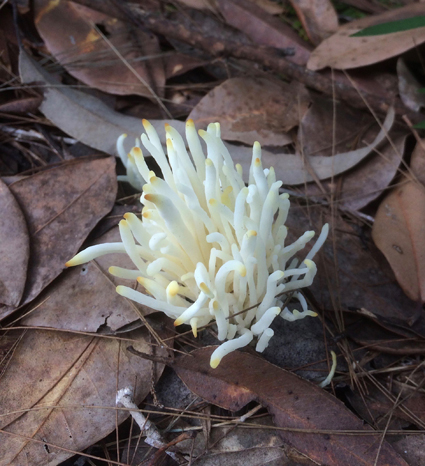

Calocera or Dead Man’s fingers

Bolettus emodensis
New Committee Member
We welcome Peter Clarke as a new member of the committee. He is well known for his work with Ku-ring-gai Council developing new programs such as the native bee hive rollout (how about coming to the talk he's giving about native bees) and pool to pond. He is a familiar face on the educational videos on EnviroTube.
Peter’s great knowledge of the Ku-ring-gai bushland and his education skills will be a great asset to STEP.
A Short History of the Coastal Sandstone Gallery Rainforest
The rainforest corridors along the gullies of northern Sydney have been called by many names as ecologists try to describe them and place them into a broader classification system, for example Temperate Rainforest (1), Sandstone Gully Rainforest (2), Coachwood Rainforest (3), Northern Warm Temperate Rainforest (4) and now more recently Coastal Sandstone Gallery Rainforest (5).
While this rainforest forms a highly recognisable ecological community, the history and evolution of the individual plant species are all quite different.
Mosses and liverworts, not the extant species, were the first land plants and appeared around 470 million years ago (Ma) in the Ordovician. It has been speculated that their impact on the earth caused an ice age because of plummeting carbon dioxide (6).
Jumping forward to the mid Devonian (383–393 Ma) and a new group of plants is present, the ferns. Most of the earliest ferns are now extinct and most of our extant ferns date from only the last 70 million years, the late Cretaceous (7). Ferns of the Coastal Sandstone Gallery Rainforest include Common Maidenhair (Adiantum aethiopicum), False Bracken (Calochlaena dubia), Umbrella Fern (Sticherus flabellatus) and tree-ferns (Cyathea species). The origin of the Cyathea tree-ferns goes back to the Jurassic (201–145 Ma) (8) but the diversity in this tree fern family is unlikely to be older than the Palaeocene (younger than 66 million years).
The Umbrella Fern and Coral Fern (Gleichenia species) are considered an ancient fern family and date from at least the early Cretaceous (9) (approx 145 Ma).
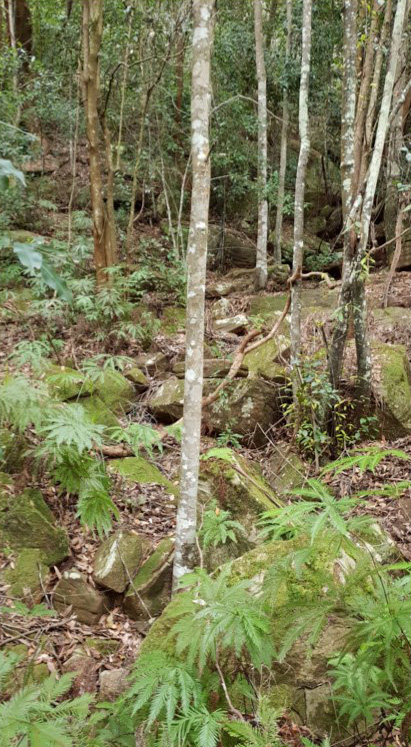

Ancestry from millions of years ago: mosses from 470 Ma, Umbrella Fern from approx 145 Ma and Coachwoods from approx 34–28 Ma (photo Robin Buchanan)
The trees that dominate the Coastal Sandstone Gallery Rainforest are all flowering plants. The earliest fossil records of a flowering plant date from early Jurassic (10), more than 174 Ma but the diversification and dominance of flowering plants occurred from the Cretaceous (145–66 Ma) to more recent times (11). The main tree families of the rainforest include Myrtaceae, Cunoniaceae and Pittosporaceae.
Myrtaceae is an enormous family that has 1646 species in Australia and 3000 in the world (12). It is also very diverse with dry fruited plants typical of dry sclerophyll, such as Eucalyptus, and fleshy fruited plants typical of rainforests. It is primarily a southern hemisphere family with considerable northern extension. Crown Myrtaceae seem to date from only 95–84 Ma (13) (mid to upper Cretaceous). Species common in the Gallery Rainforest include Narrow-leaf Myrtle Austromyrtus tenuifolia, Grey Myrtle Backhousia myrtifolia, Water Gum Tristaniopsis laurina and Lilly Pilly Acmena smithii.
The Cunoniaceae is a small family with a Gondwanan origin and seems to date back to late Cretaceous. This family includes the trees Coachwood Ceratopetalum apetalum and Black Wattle Callicoma serratifolia. Ceratopetalum and Callicoma had evolved by the early Oligocene (34–28 Ma) or earlier (14).
Pittopsporaceae, containing Mock Orange Pittosporum undulatum, seems to have originated in Australasia in the early Cretaceous (approx 117 Ma) (15).
Australia’s rainforests are a mere remnant of their former glory in the early Miocene (c23–16 Ma) when they were wide spread. By the late Miocene (10.5–5 Ma) the drying out of Australia had resulted in forests and woodlands across Australia and the remnants of the rainforests were confined to the wetter coastal areas of Australia (16).
In the northern suburbs there are also smaller stands of Coastal Warm Temperate Rainforest, Coastal Escarpment Littoral Rainforest and Coastal Headland Littoral Rainforest (5) but the Coastal Sandstone Gallery Rainforest is far the most common.
References
- Robinson, L (1991) Field Guide to the Native Plants of Sydney, Kangaroo Press
- Martyn, J (2010) Field Guide to the Bushland of the Lane Cove Valley, STEP
- Smith Ecological Consultants (2008) Native Vegetation Communities of Hornsby Shire
- Keith, D (2004) Ocean Shores to Desert Dunes, NSW NPWS
- Office of Environment and Heritage (2016) The Native Vegetation of the Sydney Metropolitan Area. Vol 2: Vegetation Community Profiles, ver 3
- Marshall, M (2012) First plants plunge earth into ice age New Scientist
- Pinson, J About Ferns American Fern Society
- Bystriakova, N et al (2011) Evolution of the climatic niche in scaly tree ferns (Cyatheaceae, Polypodiopsida) Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 165(1), 1–19
- Gonzales, J and Kessler, M (2011) A synopsis of the Neoptropical species of Sticherus (Gleicheniaceae), with descriptions of nine new species Phytotaxa 31, 1–54
- eLife (2018) Fossils suggest flowers originated 50 million years earlier than thought ScienceDaily
- Foster, C (2016) The evolutionary history of flowering plants Journal and Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales 149(1&2) 65–82
- Centre for Biodiversity Research (2002) Australian Flora and Vegetation Statistics
- Stevens, PF (2001 onwards) Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, ver 14, July 2017 (and more or less continuously updated since)
- Barnes, R (1999) Palaeobiogeography, extinctions and evolutionary trends in the Cunoniaceae: A synthesis of the fossil record PhD thesis, University of Tasmania
- Nicolas, N and Plunkett, G (2014) Diversification times and biogeographic patterns in Apiales Botanical Review 80(1) 30–58
- Australian Museum (2018) Evolving Landscapes
Photo at the top of the page: dense foliage of Coachwoods and Black Wattle in the rainforest lining the creek between eucalyptus dominated slopes (photo Robin Buchanan)
Robin Buchanan
Caring for Country
The Aboriginal heritage of northern Sydney reminds us that these precious environments around us have been valued and nurtured for thousands of years. It reminds us that people can adapt and survive significant changes in climate. It also reminds us that some things can’t be replaced or regenerated.
It could be said that Aboriginal history has only recently gained a greater following in some parts of the wider community. Modern Australian history as a whole is quite short and it is understandable that a young society would choose to focus on the positives rather than delve into what is uncomfortable. An unfortunate consequence is that when we seek to learn more, the sources of information are fewer and less detailed.
The cataclysmic loss of life as a result of the smallpox epidemic in 1789 also meant a huge loss of traditional knowledge. The following decades of policies and attitudes that were unsympathetic towards Aboriginal people meant that the comprehensive environmental knowledge of the custodians for every tree and flower and hill and creek and bay would diminish.
Much of the work to learn about and protect Aboriginal heritage has focussed on the archaeology. The rock engravings found on Hawkesbury Sandstone platforms among Angophoras and Acacias have intrigued visitors and residents alike.
What could they mean? Macropods and marine species, boomerangs and shields, human and deity figures are represented in different areas.
Some were recorded and discussed in academic journals from the mid-1800s, with names suitable to the era, such as Mankind. A government surveyor recorded hundreds of engraving sites in the sandstone country in the late 1890s.
Throughout the twentieth century various individuals from the Australian Museum and elsewhere researched and tried to urge governments and the wider population to value and protect the engravings. Some engravings were individually protected through this and local activism, as well as the thousands that were deliberately and accidentally protected in the state and local government reserve system. The role of individual Aboriginal people in these campaigns is still poorly researched.
Then there are the rock shelters. Hawkesbury Sandstone again provided a medium for Aboriginal heritage to merge with the environment. What could be a spectacular natural landscape feature could also contain the hand stencils of family members from thousands of years ago, or the painted image of an important animal or its tracks. Even the ones we have forgotten locally, like emus and koalas.
Then there are the shell middens that shine along the now rapidly eroding foreshores of the estuaries and bays of this incredible landscape. Places where families gathered year after year to share food and stories. The middens tell us what people gathered and brought back to eat. They inform us of environmental and cultural change over time with variations in species and quantity. They invite Aboriginal people to feel welcome and connected.
Could it be said that the outsider’s interest in Aboriginal heritage and culture has been aimed in the wrong direction?
What does it matter if we record the engraved images of an animal if we have not recorded the wisdom of how to protect that species or its habitat?
Is it even fair to try to capture that wisdom but not nurture the people who have developed and implemented it over such an incredible period of the earth’s history?
We cannot go back and reinvent the past, only learn from it. Some knowledge that has been lost cannot be recaptured. A rock engraving destroyed or faded away is gone forever. However, as the bush regenerators know, the seedlings that are given the right conditions today will become tomorrow’s resilient canopy.
The climate is changing and the urban bushland is under increasing pressure. The many traditions of looking after one’s local area are more important than ever.
Our thanks go to David Watts and the friendly team at the Aboriginal Heritage Office.
Photo at top of page: David Watts with group on Sites Awareness walk, late 1990s
David Watts
Geology of the Sydney Basin
Our local and regional environment owes so much to its geological heritage. We live in the Sydney Basin, an epicontinental pile of sedimentary rocks several kilometres thick that was laid down in the Permian and Triassic periods between 300 and 200 million years ago, and our present landscape framework was created by tectonic uplift and erosion of its strata.
Abundant life in a chilly sea
We might think of our local landscapes in terms of its multiple sandstone tablelands, spurs and gorges. Their rocks were mostly laid down by fresh and brackish water in flood plains and estuaries, but the early history of the Sydney Basin incorporates a strong marine influence, and you can find abundant shelly fossils in numerous sites along the coast south of Wollongong. There's also much evidence that the sea at the time was icy cold and peppered with drifting, melting icebergs, and you can still view their dropped erratic, morainic boulders nestling amongst the fossils in cliffs and rock platforms. The mineral glendonite found down there only forms today in icy-cold sea floor mud – it was named after its discovery site at Glendon on the Hunter River. The global climate conditions captured by this older Sydney Basin suite is of national significance both to our scientific heritage and to a broader understanding of the earth's history.
A great extinction event
Towards the close of that chilly, early basin epoch, the seas gradually subsided and coal formed from the peat of boreal swamp forests, contributing historically to our region's strong economic base. But the coal story came to an abrupt end 252 million years ago with the great end-Permian extinction event, when massive volcanic outpourings on the far side of the globe bathed the planet in acidic gloom and warmed and dried its atmosphere.
The evidence is beautifully preserved in cliffs south of Newcastle (pictured), north of Wollongong and also in the Blue Mountains.
This key event should be much more widely recognised and understood as its effects are mirrored in current climate change and extinctions. Our local geological heritage carries critically important environmental messages for today.
Plain old sandstones reveal fascinating stories
Some of our local sandstones were sourced from a long way off. Research on the Hawkesbury Sandstone based on radiometric dating has matched grains of a mineral called zircon with the same mineral in igneous rocks of the Transantarctic Mountains. Antarctica was joined to Australia at that time, and while still a long way off, the scale of the river system implicated is well within that of many flowing across present day continents.
Australia's membership of the supercontinents of Pangaea and subsequently Gondwana was the beginning of a story that flows right through to the roots of our floral diversity. Clearly it underpins our natural heritage.
Our sandstone's floral diversity
Our sandstone landscapes are built largely from nutrient poor but iron- and quartz-rich rocks that support an incredibly rich flora, many of whose species benefit from the buffering action of iron against phosphorus toxicity. The floral diversities of sandstone heathlands and shrublands in places like the Royal and Ku-ring-gai Chase are only surpassed in Australia by those of south-west WA, an internationally recognised biodiversity hotspot. Long term, the heritage value of our local bushland outstrips that of any of the temporary creations of human activity, however functional or beautiful they might be, and it must be preserved at all cost.
Dinosaurs, volcanoes and diatremes
The earlier paragraph on the great extinction event might also have mentioned that this kick-started the evolution of the dinosaurs, which of course ultimately led to the birds. The dinosaur era peaked in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods between 200 and 66 million years ago before ending in that other great extinction event, and at that time the sedimentary rocks of the Sydney Basin were compacting and drying out.
But there was still enough water left in their pores and joints that when basaltic magmas trickled in from depth, it flashed it into superheated steam that shattered its way to the surface at numerous points around the region. In many cases the magmas wormed their way through the crevices of shattered rock to follow it to the surface, also to be blown to smithereens by explosive pressures. The volcano style of that time is known as a maar, and its feeding pipe a diatreme.
In our northern Sydney region we have the largest and best preserved diatreme in Australia in the Hornsby quarry. This has heritage value and is a geological site of international status. Fortunately it appears the filling of the quarry for the parkland project has preserved the upper faces and cleared them of debris, thus exposing the diatreme's classic layered structure (pictured).

Layering in the volcanic debris of the Hornsby diatreme
Photo at the top of the page: Ghosties Beach Munmorah: black coal followed by white sandstone band marks the extinction event
Dr John Martyn
Timbergetting in the Lane Cove Catchment
In February 1805 botanist George Caley (sent out by Sir Joseph Banks) made an exploratory trip from Pennant Hills across the upper catchment of the Lane Cove River and reported on the fine timber. Nine months later Governor King issued directions for a gang of convicts to be employed at the North Shore to procure ship timber.
A timber carriage with eight draught bullocks was conveyed to the work site in the government punt, attended by a competent number of hands. Thomas Hyndes, one of the original grantees of land at Wahroonga, and clerk and overseer to the superintendent of camp and gaol gangs, probably accompanied them to the site on the flat at Fiddens Wharf, on the northern side of the Lane Cove River at Killara.
From an administrative point of view the Lane Cove camp was a problem. It was located distant from Sydney and run by overseers who had not been tried and tested in Sydney under the watchful eye of the principal superintendent.
There were three overseers appointed and dismissed from Lane Cove between 1808 and 1814. It was during 1809 to 1814 that the camp was most productive. The main timbers logged were Blackbutt, Blue Gum and Iron Bark for building purposes and Casuarina for roof shingles.
Governor Bligh prepared material to erect some necessary buildings including a large barrack for soldiers and timber from the North Shore Camp was used to build the Parramatta Store, completed by the end of 1809, and the Commissariat Building in Sydney, begun in 1809. These no longer exist.
Macquarie visited the camp in May 1810 and found that the timber in the Lane Cove Valley between Hornsby and Roseville was getting scarce and observed that the camp would need to be moved elsewhere.
Macquarie’s first major project using Lane Cove timber was the building of a Light Horse Barracks and a new hospital, now Parliament House and The Mint. The numbers of draught cattle at Lane Cove were trebled in preparation for this major project.

Rafters at the southern end of The Mint showing a purlin (top horizontal timber) attached to the rafter using a tusk tenon joint (photo Ralph Hawkins)
In 1814 there were two overseers at Lane Cove; one for the men and one for the stock. There were four timber fellers who supplied eleven sawyers, seven shingle splitters, eight timber carriage drivers, four stockmen, two boatmen, two blacksmiths and a wheelwright. There were also two watchmen and five other labourers, making a total of 48 men.
The hospital, completed in 1816, has some of the last timber cut at Lane Cove. Soon afterwards the camp was re-located to Pennant Hills and the North Shore was described as follows by Alexander Harris:
I could not but take notice of the immense number of tree stumps. Each one of these had supplied its barrel to the splitter or sawyer or squarer: and altogether the number seemed countless. Several times I was induced to wander off the road down a grassy slope overshadowed by oak or gum or ironbark, to where I saw the form of a hut, in the hope of getting a light for my pipe; but found only some deserted pit or falling hut, with docks and other such plants growing all around, as is usually the case when the grass has been destroyed to the very roots.
Photo at the top of the page shows timbers in The Mint that were probably sawn from timber cut in Lane Cove during 1812 and 1813; the ceiling joists are all numbered in Roman numerals (photo Ralph Hawkins)
Ralph Hawkins
Annie Wyatt’s Conservation Ethic and the National Trust
Ku-ring-gai has a rich environmental history. Some even consider it to be the birthplace of the Australian conservation movement because it was here that one resident, Annie Forsyth Wyatt, called for a National Trust (NSW) to be founded.
Gordon resident, Annie Wyatt (1885–1961) became a strong force in the emerging conservation movement, collaborating with many other key Sydney conservationists of the 1930s. Annie Wyatt was very insistent that the early National Trust (NSW) be a force in protecting the natural environment:
… to safeguard and govern the national state parks, national monuments and reserves of the state.
Annie Wyatt, grew up when there was deep concern about the loss of many of Australia’s forests. As a young woman she witnessed the ‘wanton destruction’ of the trees, bushlands, forests, woodlands and fine colonial houses on Sydney’s Cumberland Plain, when she lived at Rooty Hill as a young girl.
However, Annie Wyatt became a conservationist ‘activist’ after being incensed when she saw a Ku-ring-gai Council truck dumping garbage into the creek below her home in Gordon in 1927. Distressed, she quickly gathered her neighbours together.
This led to her forming the Ku-ring-gai Tree Lovers’ Civic League which aimed ‘to safeguard the natural charms of the municipality’ and in particular to promote Australian native trees.
The League organised school essay competitions and tree planting ceremonies that included celebrating ‘tree lover’ Joseph Maiden (1859–1925), the Director of the Botanical Gardens and a pioneer advocate for eucalyptus forests.
Underneath the magnificent lemon-scented gum tree along Henry Street, Gordon, in the Annie Wyatt Park, next to Gordon Station, lies a plaque dedicated to Mr and Mrs Charles Musson. The Ku-ring-gai Tree Lovers’ Civic League planted this eucalyptus in memory of Charles Musson (1856–1928), Gordon resident and teacher-lecturer at the Hawkesbury Agricultural College. Charles Musson was a great enthusiast for the new school subject – nature study – that was being introduced into the school curriculum in the early 20th century.
The Ku-ring-gai Tree Lovers’ Civic League inspired others to form their own tree lovers’ leagues in places such as Lane Cove, Mosman and Orange.
Annie Wyatt and the Ku-ring-gai Tree Lovers’ Civic League, went on to work with many other conservationists in the 1930s including Charles Bean (1879-1968), revered WW I war correspondent and historian, and founder of the Parks and Playground Movement. Charles Bean was active in promoting the green-belt around Sydney with parks and playgrounds including the Lane Cove and Garigal National Parks (former Davidson).
David G Stead (1877–1957), the founder of one of the first organisations to protect native wildlife (the Wildlife Preservation Society) in 1909, was supportive of Annie Wyatt’s motion to form the National Trust at the Save the Trees Conference in 1944. This conference arose from the deep concern about the massive clearing of forests happening across the country.
Annie’s son Ivor Wyatt (1915-2004) followed his mother’s conservation efforts, and became president of the National Trust working with David G. Stead’s wife, botanist and teacher-lecturer Thistle Y Harris (1902–90), to promote the flora and fauna sanctuary and environmental education centre – Wirrimbirra – at Bargo.
Annie Wyatt, was an unashamed ‘ardent tree lover’. She rejected the notion of ‘progress’ that emerged as the dominant ethos after WW II that demolished swaths of colonial buildings and land cleared massive bushland across the state.
When Annie Wyatt formed the National Trust of NSW in 1945 she wanted an organisation that would protect monuments, houses and landscapes for perpetuity. She modelled it on the English National Trust which was fighting to protect its own significant buildings, monuments and landscapes from being destroyed by encroaching industrialisation towards the end of the 19th century.
The National Trust became an important counter voice opposing the post war calls for modernity and ‘progress’ that was knocking down so much history and nature.
When Annie Wyatt saw the threat to the Dalrymple Hay Forest on Mona Vale Road, Pymble/St Ives in 1934 she worked with the ‘tree mayor of Ku-ring-gai’, Cresswell O'Reilly (1877–1954) to raise funds to purchase 11.5 acres to prevent the subdivision of Dalrymple Hay Forest, Mona Vale Road, St Ives in 1934. Cresswell O’Reilly would go on the chair the first meetings of the National Trust of Australia (NSW) formed in 1945.
Professor Eben Gowrie Waterhouse (1881–1977), of Eryldene, Gordon, also supported Annie Wyatt in this Ku-ring-gai forest campaign and presented the petition to save the Blue Gum High Forest to Ku-ring-gai Council. The community was again galvanised into campaigning to protect this unique and precious forest when it was again threatened with development from 2004–07.
Annie Wyatt’s conservation ethic continues to this day in the fight to protect Sydney’s urban bushland.
Photo at the top of the page is of the Tree Lovers’ Civic League planting in 1949 (courtesy National Trust of Australia (NSW) Archives)
Janine Kitson
Ahimsa: A Story of Bushland Protection
Walking along hand built stone paths into the bushland property Ahimsa is a step back in time and an inspiration for the future. It is also a remarkable testament to the former owner Marie Byles.
Gifted to the National Trust of Australia (NSW) over 40 years ago by Marie Byles, this 3.5 acre bushland property at Cheltenham in the Upper Lane Cove Valley is now listed as a state heritage item. Ahimsa adjoins Lane Cove National Park and is part of a large area of bushland surrounded by urban development.
Marie Byles was a visionary woman well ahead of her time. She was the first female to practice law in NSW, a mountaineer, explorer and avid bushwalker, a committed conservationist, a feminist, author, and original member of the Buddhist Society in NSW.
Marie was a passionate protector of bushland, whether from development, roads, weeds, or uncaring government officials. In 1938 she built a simple fibro and sandstone cottage on the property for her home on a rock ledge overlooking the beautiful surrounding bushland. The name of her home Ahimsa means harmlessness, a Buddhist and Hindu spiritual doctrine and Sanskrit word. This name reflects her belief that we are not separate from the world around us, and the natural environment should be respected and protected from harm.
Later in 1947, Marie designed the nearby Hut of Happy Omen which was built by friends and volunteers to accommodate a range of people and activities, including visiting Buddhists, bushwalking groups, conservationists and social gatherings.
Ahimsa is little changed in over half a century, and represents the physical expression of the life and values of Marie Byles. She left the land to the National Trust to protect its bushland in perpetuity, and in the public interest. The significance of the property is its realisation of Marie’s lifestyle and beliefs, and strong connection with current ideas about sustainable living, mindfulness, meditation and protection of the natural environment.
Ahimsa is a place that is important in the story of the conservation of Sydney’s bushland. An easy walk from the railway station, it is a place of peace away from Sydney’s hustle and bustle. The Hut of Happy Omen is available for use by people and groups compatible with the values of the property, by arrangement with the National Trust.


Friends of Ahimsa is working with the National Trust of Australia (NSW) to support future management of the property and to make Ahimsa accessible as a place that tells the story of its former owner and contributes to the realisation of Marie Byles’ dreams and values.
Children’s Art at Ahimsa on Sunday 28 April 2019 provides an opportunity for children between 7 and 11 years of age and their carers to appreciate the Ahimsa bush.
Although Ahimsa faces challenges for the future, including how to effectively maintain its bushland, heritage values and buildings, Marie Byles’ vision of simple living and protection of nature remains an inspiration. It is hoped that future generations will continue to use Ahimsa to learn about and reflect on Sydney’s bushland heritage, and the people who were instrumental in protecting it.
To find out more about Friends of Ahimsa, the conservation and management of the property, or to be placed on the Friends of Ahimsa contact list for future events and activities, please email This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..
Martin Fallding has a lifelong association with Ahimsa as a neighbour and family friend of Marie Byles. He has had a long involvement in bushland conservation and is currently the president of Friends of Ahimsa.
Camps for Girls at West Head in the 1950s
1956 was my second year out from Sydney Teachers’ College where I trained as a physical education teacher. As a young 21-year-old I was very excited to get the opportunity to apply to be seconded from the NSW Education Department to the National Fitness Council programme. The boys’ programme was run at Juno Head and Little Marley. The girls’ programme was at West Head where an army base had been built during World War II.
The programme ran from Tuesday to Thursday for one or two schools each week. A teacher from each school was asked to attend, but this seldom happened. Generally, I would have about 20 girls, but I recall one time when I had 44 girls on my own!
On Tuesday morning at 9 am the girls would come to the Nat. Fit Office with their food and clothes. I would issue each of them with a Paddy Pallin four pocket A frame canvas backpack and an ex-army groundsheet. I would then show them how to pack their tins of food and usually an enamel plate and mug.
We would then all set off to walk to York Street to catch the double decker bus to Palm Beach. The trip took an hour and a half to the old wharf on Pittwater where we caught the 12 o’clock ferry to Big Mackerel Beach. Then it usually took about one and a half hours to walk up to camp which was about 300 feet above sea level. The girls used to find it hard going as their packs often had tinned food and they were not familiar either with a bush track or carrying a backpack.
It was a very pretty walk as it wound around the steeply sloping hillside of excellent Hawkesbury sandstone flora looking opposite to the Barrenjoey tombola. Just before the final climb up to West Head there was a waterfall which had to be negotiated by sidling along a narrow ledge.
It was a steep climb up the last 150 feet to the camp at the top where a tired group of girls would be greeted by the camp caretaker Stewart Pitts and Mrs Pitts. A retired couple who had built a cottage in Big Mackerel Beach. Both had a broad Scottish accent and they always had a cup of tea in their kitchen for me.
There was no electricity at camp apart from a generator that supplied lights at night. Perishables were put in a kerosene refrigerator. The girls slept in a 30 bed dormitory of former army bunks which had a horsehair mattress on a wire base. At the southern end there was had a huge fuel stove which I recall I had to use on a couple of occasions when it was too wet to cook outside. It was extremely smoky when the fire was lit.
When they were all settled in we would have a short walk to gather firewood up the dirt road towards Commodore Heights. I would explain some of the early European history to explain where all the names came from and show them remnants of the old military occupation during World War II, when over 500 men were stationed to protect the important rail and road bridges further up the river, linking Sydney with industrial Newcastle and its strategically important steel works.
The views were and still are magnificent, looking north up to Gosford and the Central Coast, and opposite to the striking Barrenjoey Lighthouse and the old Custom House on Pittwater.
After gathering firewood for their group, they learnt how to make a tidy wood pile and later how to build a cooking fire in the grates provided near the great rock outcrops on the western side of the mess hall. As many of the girls were from inner city areas, camping and outdoor cooking and washing up were not familiar tasks.
The toilet was a pit toilet or ‘long-drop’ at the end of a pathway back from the camp. The huge septic tank from the wartime was not available then. Water came from a tank.
The first evening we had team games in the mess hall. Lights out was at 9 pm. For many of the girls going to the toilet after dark was quite scary; as were all the strange animal calls at night, especially when possums had an argument on the tin roof. For many, they had not been away from street lights and there were no outside lights at the camp. Settling down at night was quite a challenge for some!
On our second day we went out bushwalking for the day to see Aboriginal engravings or to visit the many delightful creeks, or beaches on the Hawkesbury River. Flint and Steel and Hungry beach being favourite places.
Usually we would see a koala in the trees on Commodore Heights. There was so much of interest in the history and in the vegetation and wildlife. Occasionally, we would scramble down under the old camouflage nets and steep wooden stairs to the gun emplacements near the shoreline of the river. By about 3 pm I would aim to be back at camp to gather firewood for a campfire. Making doughboys, campfire singing and skits prepared by the girls were our evening entertainment.
On the last morning after breakfast we had a general clean-up, then we retraced our steps back down to the ferry at Mackerel Beach, then across to the city bus and a walk to Bridge Street after a great time at Three Day Camp.
In retrospect, this was a great time for nature-based learning and for appreciation of our potential World Heritage, Sydney Basin Sandstone Flora and Fauna. Since the National Fitness Office was taken over by the Department of Sport and Recreation, I feel that school education has lost its appreciation of local geology, flora and fauna-based learning which was then available to a few.
Sadly, schools have generally lost the experience of the joys of bushwalking, and the intrinsic mutual benefits of understanding how our natural heritage and our human health and well-being are inter-connected with the health and well-being of our unique natural heritage.
Click here for an interesting history of pre-war attempts to develop West Head. We are thankful that appreciation of our bushland has changed!
Click here for an account of West Head’s World War II history.
Janet Fairlie-Cuninghame
Time for Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park to be World Heritage Listed
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park is part of a geographic, geologic and eucalyptus sandstone bushland arc that encircles Sydney. This 12,963 hectare national park is on the Hawkesbury Sandstone Plateau of northern Sydney. It is connected via other national parks to the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, which in turn is connected to the Royal National Park, south of Sydney.
The Sutherland Shire Environment Centre have been campaigning for the Royal National Park to be World Heritage listed for some time. They argue that the Royal has such cultural heritage importance as it marks the beginning of the global national park movement. The Sutherland Shire Environment Centre even argue that the Royal is the first national park in the world because it was the first to be called The National Park. US’s Yellowstone (1872), used the term ‘national park’ to acknowledge that it was administered by the federal government and not the state government.
Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park is also one of the first national parks in the world to be formed for the intrinsic value of nature. In 1894, it was the second national park declared in NSW. Its corporate seal – Natura Ars Dei or Nature is the Art of God – also expresses a spiritual connection to nature.
The driving force behind Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park was Eccleston Du Faur (1832–1915), a 19th century national parks advocate, adventurer and patron of the arts.
Eccleston Du Faur belonged to the 19th century Sydney intelligentsia and cultural elite who supported the creative endeavours of artists and explorers who ‘believed’ in this new land. Although born in England, du Faur was awe struck by the sandstone beauty of the Blue Mountains and Ku-ring-gai Chase. He played a key role in protecting the Blue Mountains’ Grose Valley because he believed it was one of the most beautiful places in the world.
In 1875 he employed the photographer, Joseph Bischoff, to join him, along with artist WC Piguenit, on an expedition to sketch, paint and photograph the Grose Valley, near Govetts Leap Falls. He planned to send Bischoff’s photographs to the 1876 Centenary Exposition in Philadelphia, USA. He wanted the world to see the Blue Mountains because he believed its spectacular scenery was unrivalled and even surpassed Yellowstone National Park in beauty.
Du Faur was also concerned about Sydney’s fastly disappearing wildflowers and made sure the park’s first by-laws had laws against the cutting of wildflowers. Regretfully this was not strong enough to stop the removal of 4000 waratahs, taken in one month in the post WW II years. The Trustees also prohibited the defacement and destruction of Aboriginal rock art sites and middens in the park.
Recently the Friends of Ku-ring-gai Environment (FOKE) have met with STEP to discuss how they can work together in putting forward the claim for World Heritage listing Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park – one of the first national parks in the world.
Janine Kitson
The Early Days in what is now Lane Cove National Park
The early European history of the area that became Lane Cove National Park could be said to stem from an exploratory visit to the Lane Cove River by George Caley in 1805. Caley was employed as a plant collector by Joseph Banks and was the first person to make a systematic study of eucalypts. He reported on the quality of the trees in the Lane Cove River valley and it is thought that as a result a convict timber camp was set up at what later became Fiddens Wharf.
One of the convicts employed at the camp was William Henry. He arrived in 1801 on the Earl Cornwallis, and no doubt obtained a good knowledge of the valley while working as a timber getter. After Henry was emancipated Governor William Bligh promised him a grant of 1,000 acres in an area which now includes much of the lower park and West Lindfield. Henry took up the grant and started a vineyard on a portion of the area. Unfortunately for him Bligh became somewhat distracted with the Rum Rebellion, the grant was never confirmed and eventually around 1850 Henry was thrown off the land as the government of the day prepared to sell it.
Some say that another famous Australian identity, John MacArthur had schemed to ensure that William Henry suffered because he had supported Bligh during the rebellion.
However, that was not the end of his family’s connection, his granddaughter Maria married Thomas Jenkins and in 1852 they purchased a portion of the land originally held by her grandfather. It was this family who held the property right up until 1937 when it was purchased by the government to form the basis of the national park.
The farm or orchard was known as Millwood, the house Waterview and the small stone building we now know as Jenkin’s Kitchen was built around 1855, separately from the house, as was often the case at that time when there was a fear of fire burning down the main building. Ironically the main building burnt down in 1943 after the incorporation of the area into the park, and although the kitchen has been affected by fire it is still with us.
After the recent renovations, which include a new roof and extensive work to the sandstone, there is every hope that it will remain as a focal point at the park headquarters for many years.
Invitation
Congratulations to STEP on reaching the milestone of the 200th issue of your magazine.
We at Friends of Lane Cove National Park also have a milestone coming up: the 25th anniversary of our founding. Many of you will know that this came about after the devastating fires in early 1994. However, that was not the start of bushcare in the park, a dedicated group had already been working in Carters Creek since 1991.
 On 25 May we are gathering at the park to celebrate our 25 years and also to officially open Jenkins Kitchen which Friends have renovated with the aid of a Heritage Near Me grant. The grant is particularly designed to return heritage buildings to a form that can be accessed by the public. In this case the building, which is thought to be the oldest building in Ku-ring-gai, will be used at an interpretation centre illustrating its past use as a kitchen while acting as a source of information about the flora and fauna of the park.
On 25 May we are gathering at the park to celebrate our 25 years and also to officially open Jenkins Kitchen which Friends have renovated with the aid of a Heritage Near Me grant. The grant is particularly designed to return heritage buildings to a form that can be accessed by the public. In this case the building, which is thought to be the oldest building in Ku-ring-gai, will be used at an interpretation centre illustrating its past use as a kitchen while acting as a source of information about the flora and fauna of the park.
We would like to extend an invitation to anyone who has been a volunteer in the park or member of Friends of Lane Cove National Park in the past (and who we may have lost contact with) to come along and help us celebrate.
We will meet near the park headquarters at noon. Refreshments and a barbeque lunch will be provided, and it will be a good chance to catch up with old friends.
If you intend to come, please let us know at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. to help us with the catering.
Photo at the top of the page is Jenkin’s homestead 1895 (photo Ku-ring-gai Library)
Tony Butteriss
Garigal National Park — Bantry Bay’s Early Days
Sydneysiders are lucky to have several national parks within easy reach of suburbia. Their existence is thanks to a situation where much of the land was too steep or inaccessible to build on in the early days. However the bushland was the setting for plenty of activity before its value for conservation and public benefit was recognised. Bantry Bay is a prime example.
Garigal National Park in only 8 km from the centre of Sydney. It covers about 2,200 hectares of bushland, comprising the valley of Middle Harbour Creek and its tributaries extending as far north as Mona Vale Road at St Ives, the slopes along the northern side of Middle Harbour as far as Bantry Bay and Wakehurst Parkway. The largest part is in the catchment of Narrabeen Lakes.
Bantry Bay is the only bay in Sydney Harbour that is not readily accessible from the land because of steep valleys, but access by water is a different story. Bantry Bay is the last deep water inlet to retain the character similar to that before European settlement.
The first European incursion into Bantry Bay was a bullock track, down which timber from Frenchs Forest was hauled to a wharf on the eastern side of the bay and shipped to other parts of the harbour.
In 1879 the Bantry Bay area was set aside for public recreation. By the start of the 1900s, the eastern side of Bantry Bay had been turned into a popular pleasure ground, complete with dance hall, picnic ground, a dining room and several summer houses. The Balmain New Ferry Company, operated by John Dunbar Nelson, promoted the area as a secluded, scenic and romantic retreat for the residents of an increasingly urban Sydney.
Early in the 20th century the safe storage of explosives became a concern. Bantry Bay was surveyed as a possible site because of the ease of transport by water and its seclusion. While Bantry Bay solved the thorny problem of where to safely locate a magazine complex in Sydney, it alienated the reserve from the public to whom it had been originally dedicated. Despite a storm of protest, including from the newly-created Warringah Shire Council, the land was dedicated for explosives storage in 1908.
The site was expanded over the years, in particular during World War I. The magazines were operated by the state government. They stored explosives for public works, including the Sydney Harbour Bridge and underground rail tunnels, and commercial purposes such as mining.
The site was taken over by the Allied Forces during World War II. Its final development comprised various magazines where the explosives were received, sorted and stored as well as an office, two jetties, numerous sheds and testing laboratories.
After the war, the difficulty of site access and the cost of maintenance led to the site’s closure in 1964 and since then the site has mostly been allowed to deteriorate.
 The hillside above the magazines that is covered in low vegetation in the photograph is now fully revegetated and the area is fenced off. The easiest place to see the old magazines is from the other side of the bay at Wharf picnic area.
The hillside above the magazines that is covered in low vegetation in the photograph is now fully revegetated and the area is fenced off. The easiest place to see the old magazines is from the other side of the bay at Wharf picnic area.
The buildings on the western side of Bantry Bay are architecturally significant both for their rare and specialised design and as examples of the public utility architecture of Federation Sydney, most of which is now either gone or threatened. They have been classified by the National Trust (1975).
A detailed description of the significance of the complex of buildings is set out in the draft Conservation Plan of Management (see details below). It identifies the Receiving Magazine as the most significant structure on the site but acknowledges that it may not be possible to repair. The design of the buildings is such that they cannot be adapted for a wide variety of uses without their significance being compromised. Access difficulties and the current lack of utilities may also cause problems for anyone interested in re-using the site. However they could be accessed by a trail from the Magazine Track or from a jetty.
Sources
Manly Daily (2016) The Former Explosives Complex that is now Part of a National Park
MacRitchie, J (2008) Bantry Bay, Dictionary of Sydney
Garigal National Park Plan of Management (2013) NPWS
Bantry Bay Conservation Plan of Management (draft) (2002) prepared for the NPWS by Graham Brooks and Assoc, Taylor Brammer Landscape Architects, Mary Dallas Consulting Archaeologists
Photo at the top of the page is Bantry Bay in 1972 (source Manly Daily 22 September 2017)
Jill Green
Preservation of Blue Gum High Forest in St Ives
On the high ridges north of Sydney Harbour grew a tall, open forest of blue gums, blackbutts and casuarinas with a moist understorey of shrubs, ferns, creepers and orchids. The largest remnant to survive the timber industry, orchards and spread of suburbs remains at St Ives. Threats of fragmentation necessitate repeated community campaigns to avoid further loss.
In 1925 this remnant of tall forest was purchased as a demonstration forest and named after the commissioner for forests, Dalrymple Hay.
Browns Forest which then extended to surrounding roads, was reduced by subdivision into 1 acre blocks for housing when neither the NSW government nor Ku-ring-gai Council purchased it. What remains was saved by community pressure led by Annie Wyatt of the Ku-ring-gai Tree Lovers’ League, the mayor Cresswell O’Reilly and the Forest Preservation Committee. The 11 acres without a street frontage was purchased in 1934 by council for 1460 pounds, less 310 pounds from the owners if an undertaking was given to dedicate the land as forest reserve. Council completed the purchase with 350 pounds from public donations and covenanted Browns Forest as ‘forest reserve for all time’.
In 1946 land was resumed for water storage although the reservoir was not built until 1974.
100 and 102 Rosedale Road were owned by Prof Room from 1938. He built a house on the uphill part of 102 leaving the remaining portion forested. Following the deaths of Prof Room and his wife the property was sold in 1990 and the new owners submitted to council a nine lot subdivision on the 1 hectare.
People power needed again
Ku-ring-gai Bushland and Environmental Society, the National Trust and the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service submitted objections, saying, due to the condition of the forest that the land must be purchased for conservation. Council rejected the subdivision but did not have the funds to purchase the land.
In 1997 Blue Gum High Forest was gazetted as an endangered ecological community in Schedule 1 of the NSW Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995.
In 2000 the 1 hectare was sold again and in 2002 a 12 lot subdivision was submitted to council, which was again refused. The owners appealed against council’s decision to the Land and Environment Court. The appeal was dismissed:
… because of its inability to provide a sufficient asset protection zone … and also its impact on the endangered Blue Gum High Forest ecological community.
Yet another development application was submitted in 2004 for a single dwelling on 100 Rosedale Road. By July 2005 council had rejected this development application having received 60 objections.
Strong community support was now building for conservation of all of the Blue Gum High Forest at St Ives. A coalition of community organisations, led by STEP Inc, formed the Blue Gum High Forest Group which led walks through the forest, distributed leaflets, gave talks, wrote begging letters seeking donations and lobbied council. Fortunately most councillors were by then wanting to save this 1 hectare of forest but the purchase price was over $2million.
The properties, 100 and 102 Rosedale Road, were advertised by Colliers International for sale on the international market. However, by the closing date at the end of May they had not been sold.
Meanwhile the Blue Gum High Forest Group had surveyed all the remnants of Blue Gum High Forest, and with council, submitted an application to the Commonwealth to list the Blue Gum High Forest ecological community as ‘critically endangered’. Several mayors, NSW and federal politicians, government officials and journalists were walked through the St Ives Blue Gum High Forest.
Breakthroughs in 2005
The Commonwealth Minister for Environment and Heritage announced the listing of the Blue Gum High Forest ecological community as critically endangered. NSW also upgraded the listing.
Half of the 1 hectare was purchased by NSW Rail Infrastructure to offset loss of BGHF due to railway upgrades near Hornsby.
Council agreed to apply for funds from the National Reserve System and this was supported by the Federal Member for Bradfield.
The BGHF Group had raised donations of $72,000 which impressed the councillors.
Yet again, in 2007, another development application was submitted for a house on 102 Rosedale Road and again council rejected it on the grounds of impact on the ‘critically endangered’ Blue Gum High Forest ecological community. Fortunately the Commonwealth contributed $350,000 to assist council’s purchase of this last half hectare of Blue Gum High Forest at St Ives. The whole was added to the National Reserve System which includes protected areas across Australia including national parks, nature reserves, historic sites and private land under voluntary conservation agreements.
It was time for a party. Yet another exhausting battle to prevent loss of another piece of our natural heritage from being destroyed had been won. Community care for the Blue Gum High Forest continues with bushcare groups working with National Parks and Wildlife Service and Ku-ring-gai Council. To join in contact Ku-ring-gai Council.
Click here for more details on the Blue Gum High Forest.
Nancy Pallin
The History of National Park Estates in Berowra Valley
Berowra Valley bushland stretches from south of The Lakes of Cherrybrook to the Hawkesbury River. The valley has a long history of reservation, from 1934 up to 2012. The valley currently contains a complex system of national parks, a regional park, nature reserves and an Aboriginal area.
The basis of Muogamarra Nature Reserve goes back to 1933 and this park, from Cowan to the Hawkesbury River, is still enjoyed for six weekends of the year by the public.
In 1964 Elouera Bushland Natural Park (640 hectares) was formed from bushland stretching from Boundary Road, Pennant Hills, to just north of the Riffle Range at Hornsby. For 24 years this park was managed by a group of honorary trustees appointed by the Minister of Lands. The first president of the Trust in 1964 was the Hon Max Ruddock MP, father of the present mayor of Hornsby Shire Council.
In 1987 Berowra Valley Bushland Park was gazetted. It included Elouera Bushland Natural Park but it now extended all the way to Berowra and Hornsby Shire Council was appointed trustee by the Minister for Lands.
Further land acquisitions were made and in 1998 these lands became Berowra Valley Regional Park, an area of over 3800 hectares. Because of the high value of this land, the majority of the land was reclassified as a national park in 2012 (3876 hectares). Only 9 hectares remain as regional park along some suburban interfaces, specifically to allow dog walking.
The Friends of Berowra Valley grew out of all these changes and in 2004 published A Guide to Berowra Valley Regional Park. They have also published a map of the park, available from STEP.
While Elouera Bushland Natural Park was evolving to a National Park, other areas were being incorporated into the reserve system. In 1979 Marramarra National Park, an area of 11,759 hectares, was gazetted in the northern part of the Valley, from just north of Berowra Waters to the Hawkesbury River and west to Old Northern Road.
In 1997 Mount Kuring-gai Aboriginal Area (0.6 hectares) was reserved and in 2017 a Statement of Management Intent was written to help conserve its special cultural value.
Dural Nature Reserve was reserved in 2003 from the former Dural State Forest. With additional lands added, it is now 35.58 hectares.
With the complex history of reservation go the names of many extraordinary people. Over the years many people have lobbied, collected data, and been part of the dissemination of information to the public, but to me three names stand out.
 In 1967 Dr Joyce Vickery (1908–79), a botanist with the Royal Botanic Gardens, donated over 100 acres (40.5 hectares) of land in the Hornsby Valley for inclusion into Elouera Bushland Park.
In 1967 Dr Joyce Vickery (1908–79), a botanist with the Royal Botanic Gardens, donated over 100 acres (40.5 hectares) of land in the Hornsby Valley for inclusion into Elouera Bushland Park.
John Tipper (1886–1970), an engineer, leased the land to become Muogamarra Nature Reserve in 1933 and opened it to the public in 1935. In 1987 it became the Nature Reserve of the same name managed by National Parks and Wildlife Service.
Robert (Bob) Salt was awarded a Centenary Medal in 2001 and in 2011 he was awarded an OAM for service to conservation and the environment through a range of organisations in the North Sydney region (see photo). He has worked for the conservation and effective management of Berowra Valley bushland since 1962 to the present day.
Not all the bushland in the valley is managed by the National Parks and Wildlife Service. Hornsby Council manages large areas, there is Crown land and there is an abundance of private bushland as well. More battles for the valley may be before us.
Photo at the top of the page is the opening of Berowra Valley National Park in 2012 at Crosslands: Bob Salt, Robyn Parker (Minister for the Environment), Matt Kean (Member for Hornsby) and Robert Browne (Hornsby Councillor) (both photos Noel Rosten)
Robin Buchanan
Watagans Walk was Spectacular
The participants of John Martyn’s walk in the Watagans on 5 December 2018 were treated to some great views of the coast of the upper Hunter and some magnificent rainforest. There is often not much plant variation in the rainforest understorey but not in this case. It was special to be able to see several large red cedars (Toona ciliata var. australis) that had escaped the ravages of the foresters.
Ian Kiernan AO, Founder of Clean Up Australia
Clean Up Australia was founded 30 years ago by Ian Kiernan. It is sad to hear of his death in October 2018.
While sailing in the BOC Challenge solo round the world yacht race Ian was shocked and disgusted by the pollution and rubbish that he continually encountered. Back in Sydney Ian organised a community event with the support of a committee of friends.
300,000 volunteers turned up to the first event in 1990. This simple idea of cleaning up Sydney Harbour has now become the nation's largest community-based environmental event, Clean Up Australia Day.
Clean Up the World was launched in 1993 with the support of the United Nations Environment Program. Now about 30 million people participate from 30 countries.
STEP has supported Clean Up Australia Day since 1993.
Congratulations to Ross Walker OAM
The Beecroft Cheltenham Civic Trust has been working for the local community for many years, keeping them informed about local developments, advocating for preservation of heritage buildings and the environment, organising community events and so much more.
Current president Ross Walker who has been actively involved with the Trust for the past 25 years has been recognised in the Australia Day Honours for his leadership and has been awarded a Medal of the Order of Australia in the General Division for Services to the Community.
As the Election Looms the NSW Government makes some (Small) Environmental Announcements
It is estimated that there are fewer than 21,000 koalas left in NSW. The population may have reduced by more than a quarter over the past 20 years. The species is listed as vulnerable to extinction under the federal EPBC Act in NSW.
The major reason for the decline is habitat loss with the worst areas being in the Pilliga and South Coast. NSW is a heavily cleared landscape. Almost 40% of native forests and bushland has been removed since European settlement, and only 9% of remaining vegetation is in close-to-natural condition.
Eastern Australia is one of the world’s top 11 deforestation hotspots, along with the Amazon, Borneo and the Congo according to a report prepared by the NCC and WWF. Between 1990 and 2016, at least 2 million hectares of forest and bushland in NSW have been destroyed out of the total state area of 81 million hectares.
So what is being done about this? There are a number of decisions over recent years that will make the situation worse:
- As a result of the new biodiversity laws implemented in 2017, 99% of identified koala habitat on private land can be bulldozed.
- Last November the government commenced new logging laws called Integrated Forestry Operations Approvals. The laws reduce protections for forest wildlife, including koalas. One of the worst changes is the introduction of an intensive harvesting zone over 140,000 ha of coastal forest between Taree and Grafton. The intensive harvesting zone will see large-scale clear-felling legalised on the north coast for the first time. Because most of the trees will be gone, it’s likely that most of the koalas will be too!
- In December the Premier Gladys Berejiklian gave the green light to renew the Regional Forest Agreements (RFAs) with the Commonwealth for another 20 years. RFAs are the mechanism by which the states are permitted to log native forests under accreditation from the Commonwealth. They are meant to balance the needs of the logging industry with conservation and public recreation. Conservationists argue that the RFAs have not been properly reassessed with a thorough scientific analysis of the values of native forests, for example for carbon storage and enhancement of catchment water.
NSW Koala Strategy
One positive development, albeit with limitations, is the government announcement last May of a strategy aimed at securing the future of koalas in the wild. $45m has been committed. It involves:
- setting aside 20,000 ha of state forest as koala reserves on the Central Coast, Southern Highlands, North Coast, Hawkesbury and Hunter
- transferring 4,000 ha of native forest on the North Coast to national parks
- allocating $20m to purchase prime koala habitat that can be added to national parks
However the strategy fails to commit to protecting areas known to be home to koalas from a major intensification of logging in state forests under new IFOA laws.
In early February 2019, as the election looms, some parts of the strategy have been implemented. A cattle property once used as a recreational dirt motorbike and horse recreation area has been bought by the NSW government to become part of the first national park to be gazetted in NSW in 11 years. It borders the Wollondilly River in the Southern Highlands and is about 3,680 ha. Actually 1,150 ha of this land is already protected so the addition is only 2,164 ha. There is no information about how much of this area is currently cleared and degraded from its previous use. How long before it becomes genuine koala habitat?
Great Koala National Park is a Better Idea
The National Parks Association has developed a proposal that will provide definite security for koala populations. This is for a 175,000 ha Great Koala National Park on the NSW mid-north coast, new national parks for the last remaining koala populations in southwest and western Sydney, or new national parks in other areas of known koala significance. The choice of the north coast has been confirmed as most effective by studies completed by the Office of Environment and Heritage, copies of which were obtained under Freedom of Information laws.
Funding Announced for Improvements to Popular National Parks
Another government announcement is for a $150m investment to improve access to existing national parks that includes upgraded walking tracks, better visitor facilities and new digital tools such as virtual tours and live-streaming cameras. The main investment is in the Blue Mountains and Royal National Park where visitor numbers have increased rapidly. This is all aimed at the tourist dollar, not conservation that is meant to be the main purpose of national parks.
Will there be an increase in funding for the National Parks and Wildlife Service to look after the additional reserves? After the massive cuts in funding of the service highlighted in previous issues of STEP Matters one wonders!
Removal of Feral Horses from Kosciuszko National Park has been Stopped
In December the NSW Threatened Species Scientific Committee declared feral horses to be a key threatening process because they place dozens of species at risk closer to extinction. In response a spokesman for Environment Minister Gabrielle Upton said the government was preparing a plan of management that would:
identify the heritage value of sustainable wild horse populations and set out how those will be protected while maintaining environmental values.
That goal will be impossible to achieve.
Meanwhile, in response to the passing of the Wild Horse Kosciuszko Act, the number of feral horses being removed by current methods has been reduced to nil since August 2017 even though the Act was not passed until June 2018. The Invasive Species Council has obtained data showing that the peak number of removals was 600 in 2012.
The Nationals Parks and Wildlife Service in 2016 estimated there were 6000 brumbies in Kosciuszko National Park. Scientists estimate the population may grow by up to 20% a year. The drought though is believed to have curtailed brumby numbers.
Labor has committed to repeal the legislation to protect the brumbies.
IBM Site in West Pennant Hills – What about the Koalas?
In Issue 198 of STEP Matters we described the latest application by the Hills Council through the Gateway Process to change zoning and planning conditions applicable to the former IBM site now owned by Mirvac.
In December 2018 the Department of Planning gave council the go ahead to proceed with the public consultation process without any further amendment to the current plan. They have until 31 July to get started.
One of the issues with the current proposals is that there seems to be no agreement on who will look after the forest in the E2 zone that has been agreed to by council and Mirvac. Now there might be an answer. The Forest in Danger group understands that the NSW government is looking to join the forest part of the Mirvac site to the Cumberland State Forest. The Forestry Corporation (which runs the Cumberland State Forest) ‘co-incidentally’ just put out a Draft Plan of Management. We think the two matters are linked – that the Forestry Corp may need this plan of management to be able to take on the Forest.
Now there are reports of koala sightings in the Cumberland State Forest. There is nothing to stop them wandering into the Mirvac site.
We will be watching out for council release of the documents for the consultation and what they have to say about the koalas. Ecological reports were missing from the earlier consultation.
Murray-Darling Basin Plan: Too Little, Too Late
 We have all been shocked by the mass killing of fish in the Menindee Lakes and other areas in January, the loss of wildlife and the poor water quality and quantity for communities along the Darling River. Murray Cod and other native species believed to be up to 100 years old that have survived numerous droughts have not survived this one. The politicians are blaming the drought but the causes of the severe degradation of the Darling River go back a long way stemming from the over exploitation of the water and the lack of political will to solve the problem.
We have all been shocked by the mass killing of fish in the Menindee Lakes and other areas in January, the loss of wildlife and the poor water quality and quantity for communities along the Darling River. Murray Cod and other native species believed to be up to 100 years old that have survived numerous droughts have not survived this one. The politicians are blaming the drought but the causes of the severe degradation of the Darling River go back a long way stemming from the over exploitation of the water and the lack of political will to solve the problem.
The Murray-Darling Basin covers a massive area of southeast Australia inland from the Great Dividing Range, from southern Queensland through to the mouth of the Murray in South Australia (see map).
Water extraction for irrigation commenced late in the 19th century along the Murray River with the creation of schemes by the Caffey brothers near Mildura and Samuel McCaughey in the Murrumbidgee Valley. Regulation of the Murray River system was one of the first issues addressed after Federation.
With a severe drought in the late 1960s, environmental impacts were starting to emerge as water quality had deteriorated and salinity was apparent. From the 1970s state governments undertook initiatives to manage water diversions including the definition of water entitlements, development of water markets and salinity management, but there was no interest in the fundamental issue of too much water being used.
By 1995, in response to increasing evidence of deterioration of the Basin’s river system including a massive blue-green algae outbreak in 1991–92, the Murray–Darling Basin Ministerial Council directed that a water audit be prepared to investigate the current levels of water use and potential increases across the Basin if infrastructure was developed so that all available entitlements were taken up.
The audit showed that between 1988-89 and 1992-93 the average total diversion from the Basin was 10,780 GL/year. Of this amount, over 95% was diverted for irrigation.
The report modelled the hypothetical flows of water at the mouth of the Murray. With no diversions drought conditions would have occurred in 1 in 20 years, but with the current level of diversions drought conditions would occur in 60% of years, and under full development it would occur in 3 out of 4 years.
 This graph shows the massive increase in the water used for irrigation and agriculture as revealed in the audit report. It showed that growth even in the previous 8 years had been 8%, mostly in the north for cotton growing. Not only that, there was the potential under the current management regime for usage to grow by a further 14.5% if the infrastructure capacity were installed. However use of the full entitlements would reduce the overall security of the system for individual irrigators because the levels of reserves in storages would be reduced. The full entitlements equated to diversion of 12,344 GL per year.
This graph shows the massive increase in the water used for irrigation and agriculture as revealed in the audit report. It showed that growth even in the previous 8 years had been 8%, mostly in the north for cotton growing. Not only that, there was the potential under the current management regime for usage to grow by a further 14.5% if the infrastructure capacity were installed. However use of the full entitlements would reduce the overall security of the system for individual irrigators because the levels of reserves in storages would be reduced. The full entitlements equated to diversion of 12,344 GL per year.
Environmental Impact of Current Extractions
The 1995 audit reported that the changes to the natural flow regime from the current water diversions and extractions had had a significant impact on river health. There was a reduction in the areas of healthy wetland, native fish numbers had declined in response to the reduction in flow triggers for spawning and salinity levels had risen. Algal blooms had increased in frequency in line with more periods of low flow leading to increased water temperatures and nutrient levels. The fish kills occur when the temperature changes and the algae die off and the bacteria increase reduces oxygen levels available to fish and other aquatic life.
First Plan to Control Extractions, the Cap
In 1995, the Murray–Darling Basin Ministerial Council introduced the Murray–Darling Basin Cap on Surface Water Diversions (the Cap):
to protect and enhance the riverine environment and protect the rights of existing water users.
The Cap introduced long-term average limits on how much water could be taken from rivers in 24 designated river valleys. The total Cap was 12,100 GL per year based on possible extractions in the 1993-94 year under infrastructure then available with some adjustment for the development of new diversions outside the main states of NSW and Victoria. This total extraction each year was to be adjusted to allow for actual rainfall. With the Cap in place, new developments were allowed, provided that the water for them was obtained by improving water use efficiency or by purchasing water from existing developments.
The Cap made water in the Basin a more valuable resource as it gave entitlements to its diversion more value and saw increased trade in these entitlements. The Cap was meant as an emergency measure to prevent further disasters while a long-term policy was worked out. Nearly 25 years later, it is still in effect.
The Cap is too High
The millennium drought from the late 1990s to 2010 in much of the Basin highlighted the need for continuing reform. Too much water was still being used and the environment was suffering.
In 2007, Prime Minister John Howard announced a $10b plan to improve water efficiency and to address over-allocation of water. The Water Act was passed that set up the Murray–Darling Basin Authority (MDBA) with the purpose of developing the Basin Plan. The Act’s primary objective is:
to bring water extractions back to sustainable levels in order to protect, restore and provide for the ecological values and ecosystem services of the Murray–Darling Basin
The Act should give effect to Australia’s international agreements such as the Ramsar wetlands. The ultimate source of conflict in implementation of the Act was the provision that management should optimise economic, social and environmental outcomes.
Contents of the Plan
In October 2010, as part of the preparation of the Basin Plan, the MDBA produced a report for discussion entitled Guide to the Proposed Basin Plan. The scientific evidence described in the report stated that achieving an ecologically sustainable level of take would require the recovery of between 3,856 GL ± 20% (high uncertainty of success) and 6,983 GL ± 10% (low uncertainty of success) of surface water from the current baseline development level of consumptive use of 13,623 GL. 10,900 GL of this baseline development level was extracted for irrigation and the remainder was run off stored in on farm dams.
The irrigation communities objected violently to the idea that their allocations could be reduced by so much. The MDBA and politicians buckled and in 2012, the Basin Plan passed by parliament was for a water recovery target of only 2,750 GL (by June 2019), with a program to recover an additional 450 GL of water (by 2024) to benefit South Australia through ‘efficiency measures’ (reducing water losses via infrastructure improvements rather than buying back entitlements), bringing the total to 3,200 GL.
What about Climate Change?
In preparing the Plan in 2010 the MDBA also asked CSIRO to prepare a report modelling water availability in the Murray–Darling Basin including a projection of the effects of climate change.
The assessments for climate change scenarios were made for the median model at 2030 and for the ‘dry extreme’ and ‘wet extreme’. The median projection was of a 10% reduction in Basin-wide water availability with a range of –27% (dry extreme) to +9% (wet extreme).
So not only was the Plan the bare minimum with great risk of not achieving the necessary improvement in environmental flows, there was no allowance for adjustment for the impacts of rainfall reduction from climate change.
Unwinding of Water Recovery Targets since 2012
As has become apparent the Basin Plan is too little, too late. To make matters worse the state and federal governments have been fudging the implementation of the Plan that was always going to require dedication and strict administration.
There are several instances of improper governance and attempts to water down (pun, sorry!) the Plan. A few are outlined below.
In July 2017 ABC’s Four Corners aired a story of water theft and lack of proper oversight allowed by the NSW government. Some prosecutions followed but the administration has been laissez faire.
The Four Corners report prompted the South Australia government to hold a Royal Commission. The report just released condemns the MDBA and governments for maladministration of the Water Act and calls for a separation of management and compliance.
A series of policy changes since 2012 are threatening to further undermine the possibility satisfying the objectives of the Basin Plan. The Australian government intends to amend the Basin Plan by increasing surface water extraction limits for irrigation by 70 GL in the northern Basin. After NSW and Victoria threatened to abandon the Plan water extraction limits in the southern Darling Basin were increased by 605 GL on the basis of 36 projects that improve water efficiency but so far the MDBA has failed to demonstrate that they will achieve genuine water saving. Progress in getting the extra 405 GL to South Australia seems non-existent. Water buy-backs have been halted in favour of these so-called efficiency projects.
The Menindee Lakes fish kill is another story relating to a plan to change the water flow and reduce evaporation, too complicated to explain here but another example of mismanagement. Read a report on this from the Australian Institute.
The federal and state government ministers responsible for the success of the Act have actively undermined the Plan.
Fish Strategy Killed Off
Another concerning demonstration of disregard for science is the treatment of the Native Fish Strategy. This was developed in 2001 and lays out a plan for helping the Basin’s fish communities to recover. The MDBA produced a report in 2009 showing fish stocks were at 10% of pre-European levels (0% in some parts) and the objective of the strategy was to bring this back to 60% over 50 years. It was visionary and forward-thinking – contributed to by a multitude of scientists, managers, indigenous groups and Basin communities.
But direct funding ceased in 2012 when NSW pulled out 60% of its funding. Since then, implementation of its recommendations has been opportunistic and without central coordination. Science ignored again!
Conclusion
Even before the Plan is due to be fully implemented it has been shown to be totally inadequate. Taxpayers that have already paid billions of dollars for water buybacks now have to bear the cost of river rehabilitation, clean up of fish kills and assistance to river communities. The politicians must have the fortitude to strengthen the water take restrictions. We hope the recent events will convince the sceptics and vested interests that stronger action is needed for the common good.
Uncertain Future for Streamwatch
We have been alerted to a perplexing situation by a Streamwatch volunteer. Streamwatch was established in 1990 by Sydney Water and since has been managed by the Australian Museum which runs it under its citizen science programs.
Streamwatch volunteers monitor our waterways and deliver scientifically accurate data on water quality and biology, mentor students, alert authorities on pollution events, collect litter, provide biosecurity surveillance and provide a historical record of how waterway health has tracked over time. The program engenders understanding and stewardship of our bioregion's ecosystems.
And what does it cost to run? A mere $100,000 per year. It is an incredibly cost-effective program.
Recently the Australian Museum announced that it will no longer support the program and it appears that Sydney Water will cease funding after 30 June 2019. An Australian Museum spokesperson said the museum is committed to identifying a new organisation to take over operation of the project by July 2019 but, if future funding is not assured, it will most likely close down.
Streamwatch is so much more than a data collecting exercise, in fact it's so much more than a typical citizen science program. People may think that between Sydney Water, OEH and the EPA, Sydney's freshwater systems are monitored and protected but these authorities cannot be everywhere. Streamwatch has repeatedly been the first alert organisation for pollution events. Skilled members of the public perform a brilliant service to the community. The scheme also gives school children an opportunity to engage in real hands on science.
The Australian Museum currently has around 170 volunteers testing at 160 sites in Sydney, the Blue Mountains and the Illawarra. Streamwatch groups are made up of community volunteers, TAFE and university students, council staff and high school teachers. In the last 12 months alone 796 data sets have been uploaded to the Streamwatch database making almost 5000 data points.
Streamwatch volunteers have started an online petition calling for the NSW government to ensure that the program continues. Please sign the petition.
Australia’s Population hits 25 million but who is Cheering?
Australia’s total population grew by 390,000 over the year to 30 June 2018. In August 2018 Australia’s population hit the 25 million mark. Even before that milestone was announced public concern about the rate of population growth has increasingly focused on the shortcomings of infrastructure in Sydney and Melbourne. Even the Liberal government has been canvassing the possibility of reducing the level of immigration and has established a committee to review the current level of the intake.
However the issue is still being treated as a short-term problem so we can return to business as usual once the backlog of construction has been overcome. The idea of reducing permanent immigration even by 40,000 from the recent levels of around 200,000 pa has generated fear mongering of a calamitous reduction in economic growth. This highlights the artificial situation that has been created whereby our economic growth is dependent on population growth. The touted price-adjusted GDP growth rate of 2.6% pa over the last 5 years is only 1.0% pa on a per capita basis according to Reserve Bank data.
The majority of people recognise the success of immigration in enhancing the development and culture of the country but that is not the point. No one is proposing that immigration stops altogether. In fact a large number of people leave the country each year.
Let’s put the current situation into perspective. The table below gives some historical data of past migration rates.
10 year periods (ending 30 June) | Average net overseas migration pa |
2009–18 | 221,700 |
1999–08 | 144,700 |
1989–98 | 86,500 |
This demonstrates the huge growth in net migration over the past ten years. I don’t recall the economy being a disaster last century when net migration was below 100,000 pa.
Some Facts and Figures
We need to explain some of the detail of the definition of population. Changes in population are estimated from data of births and deaths (natural increase) and net overseas migration (NOM). Every four years a census is taken to balance the books and check the accuracy of the estimates.
The calculation of NOM is not easy. The figure of NOM is made up of permanent and temporary net migration. Immigrants are counted in NOM if they have been resident for 12 out of last 16 months. Conversely if a person leaves the country they are still counted in the population until they have been out of the country for 4 months. This applies to permanent citizens and visa holders and also temporary residents.
The NOM figure for 2017–18 was 237,000 and 263,000 in 2016–17.
The government defines a cap on permanent immigration that covers the aggregate of two groups; migrants that have arrived as permanent new residents or temporary migrants already resident in Australia can be granted permanent residency. The major criteria for admission are broadly broken up into two streams based on skill or family reunion. The total cap for permanent migration is currently 190,000. The actual number approved in 2017–18 was 162,000. Humanitarian entrants come under a separate policy and total about 20,000 pa.
The government committee is currently reviewing the 190,000 cap.
Temporary Visa Holders
The count of population includes a significant number of people on temporary visas. The main categories are temporary work visas (skilled workers, recent graduates who can stay for a fixed period, and working holiday visitors), students, bridging visas and a high number of New Zealanders who can come and go as they please. It appears that there is little control of the numbers of students. The government is bowing to pressure from educational institutions for more and more fee-paying students. As at 30 June 2018 the number of temporary residents is estimated to be more than 1.8 million. Including over 500,000 students. As explained above some of these people are counted in the official population figure.
One issue with the growth in the number of students is the pressure this creates for growth in the number of permanent migrants. Most students are allowed to stay on a temporary visa for some time after graduation and many apply for permanent residency. These new residents plus the large number of recent migrants create pressure for more and more family reunion visa. The whole system is a perpetual cycle of increase.
Still all this does not mean that is impossible to slow down!
Projection of Future Growth
The Bureau of Statistics recently released a new set of projections of future population over the next 50 years. The three major sets of assumptions used are as follows.
Scenario | Net overseas migration | Total fertility rate (average | Life expectancy | |
Male | Female | |||
A | 275,000 | 1.95 | 87.7 | 89.2 |
B | 225,000 | 1.85 | 83.0 | 86 |
C | 175,000 | 1.65 | 83.0 | 86 |
Current experience | 1.8 | 80.4 | 84.6 | |
The ABS has been instructed to assume continuation of high rates of immigration. Scenario B represents approximately the experience over the past ten years.
The projected outcomes are as follows for Scenario B.
Location | Projected population at 30 June (millions) | ||
2017 | 2036 | 2066 | |
Australia | 24.6 | 33.2 | 42.6 |
Greater Sydney | 5.1 | 7.0 | 9.7 |
Greater Melbourne | 4.8 | 7.0 | 10.2 |
Greater Brisbane | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.8 |
By comparison the NSW government is working with an assumption of a population of 6.7 million for Greater Sydney by 2036 and the Victorian government is assuming 6.5 million for Greater Melbourne by 2036. There is a chronic under-estimation of the proportion of migrants, particularly students moving to Sydney and Melbourne.
Based on these projections governments are expecting the country to provide for an extra 8.6 million citizens over the next 20 years and a further 9.4 million over the following 30 years. That’s the creation of another one and a half Sydneys in only 20 years! Where will all these people live? This is a huge imposition on our fragile ecosystems and water supply and the demand for capital to finance the infrastructure needs.
The population debate is still dominated by commentators arguing that migration has been great for the country citing various success stories. This misses the point that it is not a simple black and white issue. Of course business and the construction industry are in favour of more and more growth but that ignores the views of current citizens who cannot visualise what the country will be like with that many people.
Planning is being done in short-term bursts, a few apartment blocks here, densification of some low-density housing areas with loss of trees, clearing of bushland on the fringes of towns and cities. We are in denial of the effect short-term decisions have on longer term outcomes. The longer the high growth continues the harder it is to cut back on employment dependent on growth such as construction and education. The existing residents of Sydney and Melbourne are suffering from congestion. We need a broader discussion.
Can Stabilisation be Achieved?
Back in 1998 the ABS did a projection of the conditions under which population would stabilise. This showed that net migration of 70,000 pa would lead to stabilisation at 23.5 million in about 2050. We are miles off that figure now and the net migration figure would need to be lower to achieve stabilisation in any foreseeable timeframe.
The Small Patch of Bush over your Back Fence might be Key to a Species’ Survival
It may not look like a pristine expanse of Amazon rainforest or an African savannah, but the patch of bush at the end of the street could be one of the only places on the planet that harbour a particular species of endangered animal or plant.
Our newly published global study of the conservation value of landscapes in 27 countries across four continents has found these small patches of habitat are critical to the long-term survival of many rare and endangered species.
In Australia, our cities are home to, on average, three times as many threatened species per unit area as rural environments. This means urbanisation is one of the most destructive processes for biodiversity.
It tends to be the smaller patches of vegetation that go first, making way for a housing development, a freeway extension, or power lines. Despite government commitments to enhance the vegetation cover of urban areas and halt species extinctions, the loss of vegetation in Australian cities continues.
This story plays out all over the world day after day. Of course, it’s not just an urban story. Patches of rural vegetation are continually making way for, say, a new pivot irrigation system or a new mine to provide local jobs.

Mostly, policymakers and scientists do not consider these losses to be, on their own, a fatal blow to the biodiversity of a region or country. Small, often isolated patches of vegetation are considered expendable, tradeable, of limited ecological value due to their small size and relatively large amount of “edgy” habitat. Wrong.
Research forces a rethink
Our study analysed the relationship between conservation value of vegetation patches and their size and isolation in landscapes across Europe, Australia, North America and Africa. The findings prompt a rethink of long-held views about the relative importance of small, isolated habitat patches for biodiversity conservation. We show that these patches often have unique ecological and environmental characteristics.

That’s because they are the last patches left over from extensive clearing of flat, fertile land for agriculture or urban growth close to rivers and bays. They often contain habitats for rare or endangered species that have disappeared from the rest of the landscape. This makes these small, isolated patches of habitat disproportionately important for the survival of many species.
Our study calls for a rethink of urban planning and vegetation management regulations and policies that allow small patches of vegetation to be destroyed with lower (and often zero) scrutiny. We argue that the environment is suffering a death by a thousand cuts. The existence of large conservation reserves doesn’t compensate for the small patches of habitat being destroyed or degraded because those reserves tend to contain different species to the ones being lost.
The combined impact of the loss of many small patches is massive. It’s a significant contributor to our current extinction crisis.
Why are small patches seen as dispensable?
A key variable used in decisions on vegetation-clearing applications is the size of patch being destroyed. Authorities that regulate vegetation management and approve applications are more permissive of destruction of small patches of vegetation.
This is partly due to a large body of ecological theory known as island biogeography theory and subordinate theories from metapopulation ecology and landscape ecology. These theories suggest that species richness and individual species’ population sizes depend on the degree of isolation of the patch, its size and the quality of the habitat it contains.
While it is crucial that we conserve large, intact landscapes and wilderness, the problem with conserving only large and well-connected patches of high-quality vegetation is that not all species will be conserved. This is because some species exist only in small, isolated and partially degraded habitats, such as those characteristic of urban bushlands or remnant bush in agricultural areas.

For this reason, we highlight the importance of protecting and restoring habitats in these small isolated patches. And these areas do tend to be more vulnerable to invasion by weeds or feral animals. If the impacts of invasive species are not managed, they will eventually lead to the destruction of the habitat values and the loss of the species those habitats support.
Small and isolated patches of vegetation on the urban fringe are under enormous pressure from human use, pets, escaped seed of Agapanthus and the many other invasive species we plant in our gardens. These plants spread into local bushland, where they outcompete the native plants.
Communities can make a difference
As well as these perils, being on the urban fringe also brings opportunity. If a remnant patch of vegetation at the end of the street is seen to be of national environmental importance, that presents a great opportunity to channel the energies of community groups into conserving and restoring these patches.
A patch that is actively cared for by the community will provide better habitat for species. It’s also less likely to fall foul of development aspirations or infrastructure projects. The vicious cycle of degradation and neglect of small patches of habitat can be converted into a virtuous cycle when their value is communicated and local communities get behind preserving and managing them.

Urban planners and developers can get on board too. Rather than policies that enable the loss of vegetation in urban areas, we should be looking at restoring habitats in places that have lost or are losing them. This is key to designing healthy, liveable cities as well as protecting threatened species.
Biodiversity-sensitive urban design makes more of local vegetation by complementing the natural remnant patches with similar habitat features in the built environment, while delivering health and well-being benefits to residents. Urban development should be seen as an opportunity to enhance biodiversity through restoration, instead of an inevitable driver of species loss.
Brendan Wintle, Professor Conservation Ecology, University of Melbourne and Sarah Bekessy, Professor, RMIT University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
New Book on Coups Creek
Frances O’Brien worked as the Environmental Officer at Wahroonga Waterways Landcare for four years and has written a book about this E2 zoned conservation area. It covers an area along Coups Creek that is the headwaters of the Lane Cove River. It includes stories about the native flora and fauna, conservation work and history of the site. It is 96 pages, A5 with a fold out A4 walking trail map. Cost $21 plus postage.
This bushland land area behind the SAN hospital has improved remarkably with the large number of volunteers working on rehabilitation.
Contact Frances at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. for more information.
Lane Cove National Park to Gain some Land near M2
Lane Cove National Park will be expanded, albeit marginally, with the addition of 0.6 ha near the river at North Ryde near the Epping Road bridge below the business park.
The announcement from NSW Environment Minister Gabrielle Upton states that it will help foster habitat and threatened species along the river. The threatened species include Darwinia biflora, a shrub only found in Sydney’s northern suburbs. Weeds are a problem in this area because of the steep terrain.
Introductory Bush Walks are Popular
We have conducted two introduction to bushland walks this year, one in Sheldon Forest/Rofe Park and the other along the STEP Track. They have been well received. Peter Clarke has given interesting explanations of the ecological features of our local bushland and the importance of preserving this biodiversity. We plan on running these walks every couple of months and extend them, not far away, into the Hornsby area.
Powerful Owl Coalition
STEP is one of a group of environmental organisations that has got together to write a position paper on the habitat needs of the Powerful Owl. This iconic bird is a keystone species for maintaining ecological balance in our bushland.
We now will be recruiting other groups to help disseminate the report to all areas where Powerful Owls live.
New IPCC Report Highlights the Urgent Need for Action to Reduce Carbon Emissions
The speaker at STEP’s AGM on 30 October was Lesley Hughes, Distinguished Professor of Biology from Macquarie University, who has been studying the impacts of climate change on ecosystems for many years. She has been a leading contributor to reports produced by several expert bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and Australia’s Climate Commission. She gave a stark outline of the changes to ecosystems that have been happening and the prospects in years to come under the possible scenarios for temperature increases.
The global body assessing the issue of climate change is the IPCC. Their reports are published after rigorous analysis of thousands of scientific reports.
Early in October the IPCC released a special report commissioned at the breakthrough 2015 summit that brokered the Paris climate agreement. It sets out the key differences between the Paris agreement’s two contrasting goals: to limit the increase in global temperatures over pre-industrial levels (mid-nineteenth century) to ‘well below’ 2°C, and to ‘pursue efforts’ to limit warming to 1.5°C. The agreement also aimed to increase the capacity of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change and provide finance for measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Emissions Reduction Commitments
The 196 countries signing the agreement made statements of commitments to reduce emissions by 2030. However the national pledges that have been made are not enough to remain within a 3°C temperature limit let alone a 2°C limit. They are not even enforceable. The only result of not meeting the commitment is to be named and shamed.
Australia’s commitment was a reduction of 26 to 28% below 2005 levels. We were making progress towards that goal when the carbon tax was introduced but we have gone backwards since 2014 with a reduction of only 11% by 2017. With current policies we haven’t a hope of meeting the goal.
What is the Expected Impact of 1.5°C of Warming?
Although the Paris agreement aims to hold global warming as close to 1.5°C as possible, that doesn’t mean it is a ‘safe’ level. In 2017 the increase in global average temperatures reached 1°C. Communities and ecosystems have already suffered significant impacts from extreme weather events and drought. If the planet continues to warm at the current rate of 0.2°C per decade, we will reach 1.5°C of warming by around 2040.
But there is a lag between the timing of carbon emissions and temperature increases. The IPCC uses the concept of a carbon budget, the projection of the quantity of emissions that can occur in order to limit warming to a certain level. At current emissions rates, within the next 10 to 14 years there is a two-thirds chance we will have used up our entire carbon budget for keeping to 1.5°C. It is inevitable that temperatures will increase by more than 1.5°C unless policies are implemented now to reduce emissions drastically as quickly as possible.
What Difference does 0.5°C Make?
Impacts on both human and natural systems would be very different at 1.5°C rather than 2°C of warming. The report tries to quantify the differences to give a tangible scale to the information. For example:
- The proportion of the global population exposed to water stress could be 50% lower than at 2°C. Food scarcity would be less of a problem and hundreds of millions fewer people, particularly in poor countries, would be at risk of climate-related poverty.
- At 2°C extremely hot days such as those experienced in the northern hemisphere this summer, would become more severe and common, increasing heat-related deaths and causing more forest fires. Extreme heatwaves will be experienced by 14% of the world's population at least once every five years at 1.5°C but that figure rises to more than a third of the planet if temperatures rise to 2°C.
- But the greatest difference would be to nature. Insects, which are vital for pollination of crops, and plants are almost twice as likely to lose half their habitat at 2°C compared with 1.5°C.
- More than 10% of corals have a chance of surviving if the lower target is reached but 99% could be lost at 2°C, a disaster for the Great Barrier Reef. It is notable that the bleaching events in the last two years have killed about 50% of the coral in the Great Barrier Reef.
- Sea-level rise would be 10 cm higher by 2100 with the extra 0.5°C. That doesn’t sound much but it would affect 10 million more people by 2100 and the number affected would increase substantially in the following centuries due to locked-in ice melt.
- Marine fisheries would lose 3 million tonnes at 2°C, twice the decline at 1.5°C.
- The Arctic has been warming two to three times faster than the world average. Sea ice-free summers would come once every 100 years at 1.5°C, but every 10 years with half a degree more of global warming leading to greater habitat losses for polar bears, whales, seals and sea birds.
Fundamentally the message is that it is worth the effort to implement the measures necessary to keep warming below 1.5°C.
Can we Limit Warming to 1.5°C
Put simply, it is not impossible that global warming could be limited to 1.5°C. But achieving this will be profoundly challenging. If we are to limit warming to 1.5°C, we must reduce carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gas emissions by 45% by 2030, reaching near-zero by around 2050. Most economists say putting a price on emissions is the most efficient way to do this.
By 2050, 70 to 85% of electricity globally will need to be supplied by renewables. Lesley Hughes pointed out that 90% of current coal reserves and 85% of gas reserves will have to stay in the ground. Transport will need to convert to electric vehicles and much greater use of public transport. Sustainable agriculture is a puzzle to be solved.
Reducing commercial, manufacturing and household energy demand is an important part of the equation. Reducing food waste, improving the efficiency of food production, and choosing foods and goods with lower emissions and land use requirements will contribute significantly.
Carbon dioxide removal technology will also be needed to remove greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. But the IPCC’s report warns that relying too heavily on this technology would be a major risk as it has not been used on such a large scale before. Carbon dioxide removal is an extra step to keep warming to 1.5°C, not an excuse to keep emitting greenhouse gases.
Taking such action as soon as possible will be hugely beneficial. The earlier we start, the more time we have to reach net zero emissions. Acting early will mean a smoother transition and less net cost overall. Delay will lead to more haste, higher costs, and a harder landing.
Australia Government’s Response
Australia does not have a credible emissions reduction policy and they no longer have a body that can provide independent scientific advice on the response to climate change. Lesley Hughes was a member of the Climate Commission that was established by the Gillard government but was abolished by Tony Abbott. It was replaced by the Climate Change Authority that has been progressively stripped of scientific expertise and funding by the current government.
The government has decided to remove any emissions reduction target from the highly fraught energy policy and we still don’t have a remotely credible long term electricity policy. The other major economic sectors that need to reduce emissions, such as transport and manufacturing have been put in the too hard basket. The Emissions Reduction Fund is a farce.
Prime Minister, Scott Morrison (and the mining industry) rejected the findings of the IPCC report that coal-fired electricity must be phased out by 2050. Voters at the recent Wentworth by-election disagreed. The next election is due in 2019. We all need to tell the candidates that we want action now!
Note that there is still a body providing expert advice to the public on climate change. The crowd-funded Climate Council was established in 2013 in response to the Government’s abolition of the Climate Commission. Professor Lesley Hughes is one of this body’s councillors.
Bayview Golf Course Developer Trying Again
We recently reported on the application for development on Bayview Golf Course for seniors housing units in an area that is a core wildlife corridor and habitat for several threatened species such as the Powerful Owl and microbats. The development has been strongly opposed by Northern Beaches Council and local residents.
In August the next application for approval went before the Regional Planning Panel. It was resoundingly knocked back basically because it is over-development. The built form would be incompatible with the existing and desired future character of the area. It would have substantial adverse impact on the biodiversity of the area given that it is mapped as high priority biodiversity conservation land in the Pittwater LEP. Bat ecologist Glenn Hoye stated in a submission that subdued lighting would be required and directed to walkway areas but this would be incompatible with OH&S requirement for seniors housing.
This type of development requires a Site Suitability Certificate before further formulation of a proposal can go ahead. This certificate was provided by the Planning Department back in 2017. A freedom of information application has revealed that internal advice within the department recommended against granting the certificate because the type of development proposed was not consistent with the required zoning.
However the developer is trying again by appealing to the Land and Environment Court.
Unfortunately it is too late to send a letter objecting to the development but you can sign the petition and read more about the issue.
More Bad Decisions by the NSW Government
In recent months there have been several more bad policy decisions by the NSW government that go against scientific common sense. Under this government many environmental protections have been reversed. The election in March 2019 will be critical in turning around this adverse situation. Here is a brief summary of the major recent decisions.
1. Backflip on the Sydney Marine Park Sanctuary Zones Proposal
The only NSW coastal region that currently does not have a marine park is the Hawkesbury Shelf marine bioregion that stretches from Newcastle to the Wollongong coastal waters. A long process of campaigning and consultation has been undertaken on the creation of a park. Finally an announcement was made on consultation on a draft marine park plan. The proposal included fully protected sanctuary (no fishing) zones that covered only 2.4% of the marine area including estuaries and other protected zones that restrict line and spear fishing.
A group of recreational fishers protested vocally blowing the restrictions all out of proportion. The Minister for Primary Industries promptly decided to withdraw the sanctuary zones from the plan. A knee jerk reaction that threw out the window all that scientific consultation and discussion. Evidence shows that sanctuary zones are essential for preserving and restoring the marine estate for future generations.
The draft plan provided limited protections even before the backflip. In addition to the conservation areas covering only limited areas, these zones would allow taking of lobster and abalone. Lobsters are important for controlling the numbers of sea urchins that devour kelp that are a vital source of food for many species. The increase in sea temperatures from climate change is already causing a boom in sea urchin populations.
Consultation on the draft marine park plan closed at the end of September.
2. Raising Warragamba Dam Wall
In the Issue 192 of STEP Matters we described the pointlessness of the claim that raising the Warragamba Dam wall will provide flood protection for the Hawkesbury Nepean Valley. There are five other rivers below Warragamba Dam that flow into the valley. The wall-raising proposal will cause huge damage to the pristine wilderness and wild rivers of the World Heritage Blue Mountains National Park, drown several Aboriginal cultural sites and destroy threatened plants such as a significant proportion of what remains of the critically endangered Camden White Gum Forest and the habitat of the Regent Honeyeater.
An environmental impact and economic assessment has not been done but last month the government passed legislation to change the National Parks Act to allow inundation of the park, a first step to facilitate the proposal. Everybody is saying that the real reason for the plan is to reduce the risk of flooding of all the new homes that the government wants to build in the North West Growth Centre. But that cannot be 100% assured by raising the dam wall. Flood data experts argue that management of the water level in the dam and even using the idle desalination plant would be more effective and less costly.
3. Protection for Feral Horses in Koscuiszko National Park
This issue was covered in STEP Matters, Issue 196. The government is ignoring protests from people concerned about the welfare of the horses as well as the damage they are doing to the sensitive alpine vegetation. The opposition parties have vowed to repeal the legislation if elected. A walk is currently being held from Sydney to Mt Kosciuszko to raise awareness of the issue.
4. Proposal to Revoke the Murray Valley National Park Status
A National MP has presented a private member’s bill in parliament that would delist the Murray Valley National Park. This would open up the area for logging of the river red gums. Only 5.5% of Riverina bioregion is protected compared to the international target of 17% for each region. The bill is unlikely to be debated before the state election but it sets a terrible precedent.
These recent developments are on top of previous bad decisions such as removal of land clearing controls or their replacement with weak offset provisions. 99% of identified koala habitat on private land can now be cleared without restriction. There is already evidence of the predicted increase in land clearing even though the act only came into operation in August 2017. A study commissioned by the NCC and WWF of satellite images of north-western NSW covering the Moree and Collarenebri areas showed that the area cleared in 2017–18 was triple the area in 2016–17.
The NSW government has announced funding for purchasing koala habitat from private landowners and conversion of unproductive state forests to conservation but this is not considered enough to make any difference to the need for secure habitat. A Koala national park is a must.
IBM Site in West Pennant Hills – Another Gateway Application
Issues 193 and 194 of STEP Matters give a rundown of the convoluted application process by the Hills Council through the Gateway process to change zoning and insert site specific conditions that vary the normal development control plan conditions to facilitate the development by Mirvac of the former IBM business site next to Cumberland State Forest.
There have been further iterations of the zoning plan but we cover only the latest application here. The main positive change is the recognition of the high quality bushland by providing for the possibility of an E2 zoning (Environmental Conservation) that does not permit any residential development.
The current development proposal includes construction of 600 dwellings but the zonings will allow further development of the site.
In September the Hills Shire Council has again written to the Department of Planning requesting an amendment to the current Gateway Determination.
 The latest zoning application looks like this.
The latest zoning application looks like this.
The Forest in Danger group has sent a detailed letter to the Department of Planning objecting strongly to the latest application.
They have also requested that those concerned about the Mirvac proposals convey their objections via email.
The main points of objection to the latest proposal are as follows.
- Even though council and Mirvac have both now theoretically agreed to the forest being protected by E2 Environmental Management zoning, thanks to the outcry by supporters, there is still no formal agreement as to who will own the forest or who will pay for its upkeep. It's been over a year since E2 first appeared on plans yet Mirvac still haven't confirmed an owner for the forest. The E2 zone includes the critically endangered Blue Gum High Forest and endangered Sydney Turpentine Iron Bark Forest.
- There is a Powerful Owl nesting site near to the proposed high density residential area (zone R4) but the required ecological assessment has still not be provided. The current documents also do not make it clear that bushfire APZ will be clear of the Owl’s roosting and nesting areas.
- The medium and high density zoned areas have been extended into areas that include a major tributary of Darling Mills Creek that flows into the Parramatta River and the natural forest regrowth area to the north of the site. The maps do not show any dwellings on these areas currently. What is the reason for the extension of these zones if they are not going to be used for development? The E2 zoning should continue to apply to provide a buffer with the Cumberland State Forest.
- It is proposed that the playing fields be covered with synthetic turf but no ecological assessment has been provided on the impact of runoff into the forest and waterways and any risk in the case of bushfire.
- Previous statements were made that Mirvac would provide a community facility in association with the area of open space but this is no longer part of the proposals. A facility will be badly needed for a large development like this that is touted.
- The previous Gateway Determination required a contribution be made towards state public infrastructure because of the extra population from the development being added to the Cherrybrook Planning Precinct. No commitment has been made.
- The department has refused to allow site-specific provisions for this site yet council is asking again to allow lot sizes of only 86 m2. These sites will be only 4 m wide to house a three bedroom home. This will create an undesirable precedent. No urban design analysis has been provided to demonstrate that medium density units within a lot size of only 86 m2 will fulfil the standards of amenity through adequate setbacks, landscaping, solar access and private outdoor space.
Northern Beaches – Not Another Tunnel!
The NSW government wants to bulldoze a large tract of community land around Flat Rock Drive to construct the Northern Beaches tunnel. Another tunnel for private vehicles, but not trains, is crazy. Haven’t they learnt the lesson that the traffic will rapidly expand to clog the new road? We have to get more people into public transport!
Just like West Connex, the construction and operation will come at great environmental cost. They are proposing to use either the baseball diamond area in Bicentennial Reserve on Flat Rock Drive or the Flat Rock Gully bushland on the other side of the Drive.
Both are important open spaces used by many groups in the community. Here are just a few of the known negative impacts of the tunnel construction.
- Around 6 acres of well-used community space will be taken over by tunnel construction.
- Flat Rock Gully is a critical wildlife corridor and is recognised for its biodiversity and as one of the last refuges for our fast disappearing small native bird population. It also provides a habitat for foraging Powerful Owls, Swamp Wallabies, lyrebirds and many other native animals.
- Willoughby City Council and many dedicated volunteers have worked for 25 years to remediate this bushland.
- There is no guarantee that the Flat Rock Gully site will be returned to bushland. The RMS has offered to leave buildings and cleared areas to be used for other purposes.
- The RMS has advised that there will be over 70 truck movements an hour carrying contaminated spoil through already congested local roads and near local schools.
- The tunnel will be dug through toxic fill from the old tip site. The ground is unstable and the tip is known to contain asbestos and other toxic material.
- There will be risks of air, land, noise and water pollution from the tunnel activities to nearby homes and schools and more broadly to the Willoughby district and surrounding areas including Middle Harbour.
See the fact sheet for environmentalists. This site explains how you can act to oppose the proposal. However the consultation period has now closed.
This information comes courtesy of WEPA (Willoughby Environment Protection Association)
Book Review – Sydney’s Rocks and Trees
Such a simple title for such a comprehensive book – the subtitle ‘A photographic journey through the rich and varied geology, scenery and flora of the Sydney region’ elaborates on the topic of this lavishly illustrated volume.
More precisely, the work focuses on the Triassic sedimentary rocks of the Sydney Basin and younger volcanic and sedimentary deposits (including Jurassic diatremes and intrusions, Paleogene and Neogene basalt flows, and Cenozoic unconsolidated sediments) and the diverse flora these lithologies support.
Not since the compilation by Herbert and Helby (1980) – now out of print – has such a useful guide to the rocks of the entire Sydney Basin been published. The two publications are entirely complementary, with only the stratigraphic nomenclature for the Triassic succession and the geology of the younger rocks being common to both. In wanting to keep his book to a manageable size, Rocks and Trees barely touches on the underlying Sydney Basin Permian rocks that are covered in detail by Herbert and Helby (1980), whereas the geobotanical aspects explored in Rocks and Trees were never considered in the earlier publication.
A further obvious distinguishing feature is the prolific use of colour throughout Rocks and Trees, in which almost every page carries at least one colour image, be it of rocks, trees, flowers or even a butterfly. All photographs bear informative captions relating the landforms to the stratigraphy or intrusive unit, or the flora to the lithology. With the floral communities and the rocks they grow on being so extensively depicted in photographs taken by the author over 14 years, Rocks and Trees has definite appeal to anyone interested in geology or botany, or just keen on bushwalking.
John Martyn is a trained geologist, with 40 years fieldwork experience around the world. His observation of the wildflowers in Western Australia in full bloom sharpened his initial interest in the relationship between botany and geology. After moving to Sydney his love of bushwalking developed an appreciation of the differences in distribution of flora depending on their geological substrates.
There is clearly a need for such a book; as the author points out in the Introduction (p 7), botanists (particularly those investigating the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area, which was nominated for World Heritage status on the basis of its botany, not – surprisingly – its geology and geomorphology) have identified and formally named floral communities such as Blue Mountains Shale Cap Forest and Shale Sandstone Transition Forest, recognising their links to the geological substrate (but not the precise geological formation). John also mentions the unfortunate misuse (not only by botanists) of informal terms such as ‘Wianamatta Shale’ that has crept into the literature in some popular guidebooks.
Dr Martyn opens his account of the geology of the Sydney Basin by firstly considering the geomorphology in a chapter on Landscapes and Panoramas. Several panoramic images are annotated with the names of prominent geographic features to help orientate the reader, and the location and viewing direction of many of these scenes are plotted on a simplified geological map of the Sydney Basin (p 27). Then follows a Geological Overview, including a brief discourse on the tectonic and structural history of the basin, before the main section (amounting to roughly half of the book) which progresses up-section through the Narrabeen Group, Hawkesbury Sandstone and Wianamatta Group.
The chapter on Jurassic igneous intrusions and diatremes follows, covering dykes, sills, laccoliths and various alkaline intrusions such as Mt Gibraltar, before documenting several of the better known diatremes. New distribution maps, adapted from the Sydney Basin 1:500,000 Geological Map compiled and published by the Geological Survey of NSW more than 50 years ago, accompany each of these chapters. Cenozoic volcanic activity at Mt Tomah and Mt Banks, Mt Wilson and Mt Hay, Nullo Mountain and Robertson Nature Reserve is dealt with in the subsequent chapter.
The next section focuses on the Lapstone Structural Complex and its geomorphological expression, and illustrates how the monoclinal warping and associated faulting has caused the development of lakes and swamps that support their own distinctive vegetation. Then follows a chapter (covering 40 pages) looking in some detail at Cenozoic sands, clays, gravels and laterites in the area of the Cumberland Plain (bounded by the Hawkesbury-Nepean catchment to the west and north) and extending to coastal dunes on the central coast, laterites at Long Reef and the Royal National Park south of Sydney.
And if by this stage the reader craves still more examples of the close bonds between rocks and plants, the illustrated part of the book concludes with a chapter on Rock-loving plants, featuring some exquisite rock orchids.
A Glossary of geological terms, listing of References and an Index provide the finishing touches.
I can thoroughly recommend this book. The text is engaging to those well-versed in geology and botany, but will also be readily understood by readers with only a rudimentary knowledge of rocks and trees. Though I have lived in the Sydney Basin for most of my life, and thought that I was reasonably well acquainted with the geology of the region, I was definitely impressed by the amount of new information that I gained in reading this volume, especially from the many photos of outcrops in places that I have not visited. Identifications of the trees, native shrubs and their flowers are an added bonus.
Although the A4 page size of the volume and its weight means that it is not the sort of book that can be readily carried around in a backpack or pocket, it can certainly be taken in the car to the field. Rocks and Trees is not a coffee table showpiece but rather a practical guide to understanding the relationship of flora to geology. It should certainly occupy a place on the bookshelf of any geologist (or botanist for that matter) living in the Sydney Basin or who visits the area regularly or occasionally.
John Martyn is an accomplished photographer and experienced author, having self-published several books previously (including Sydney’s Natural World, Field Guide to the Bushland of the Lane Cove Valley, and Understanding the Weather) through STEP Inc., a local community-based group concerned with (amongst other things) environmental education and the preservation of the natural habitat of Sydney’s upper North Shore. All his books are meticulously edited (by fellow members of STEP) and beautifully produced on high quality paper, and Rocks and Trees is no exception.
The price is another pleasant surprise: $60 plus postage. STEP members save 30%, reducing the cost to just $42. I understand the print run is not very large (certainly not in normal commercial quantities) so it would be worthwhile investing in this book now before it sells out. Order your copy now!
Reference
Herbert, C. and Helby, R. (eds) 1980. A Guide to the Sydney Basin. Geological Survey of New South Wales Bulletin 26, 603 pp.
Reviewed by Ian Percival (Pymble, NSW)
Help Save the Bylong Valley from a New Coal Mine
This is not a recent issue. The process of approval of this mine application by Korea Electric Power Company (KEPCO) started three years ago but now it is coming to the crunch decision time.
The development application and environmental impact statement were placed on public exhibition in 2015 and received 364 submissions, of which 336 opposed the project. It was referred to the then Planning Assessment Commission for a merit review, which raised concerns about the mine's heritage impacts on Tarwyn Park – a farm internationally recognised as the site where natural sequence farming methodologies were developed. The property was developed by environmental pioneer, Peter Andrews, but KEPCO purchased this property and many others along with the school, general store. The review also found uncertainty and incomplete information about the risks and benefits of the project.
The NSW Department of Planning and Environment has now completed its final assessment report of the current plans and said the development is approvable, subject to stringent conditions. Following advice from the state's Heritage Council, the department said it placed appropriate conditions on the development to protect the heritage of Tarwyn Park, including a prohibition on open-cut mining on the property. But the mine will go right up to the boundary of the property! Who will want to live there and look after the land?
The matter has been referred to the Independent Planning Commission which will hold a public hearing this month before making its final determination. As the former Planning Assessment Commission has already held a public hearing in relation to the project, merit appeal rights in relation to any future determination by the renamed Independent Planning Commission have been extinguished.
This mine should not proceed because:
- The entire landscape of the Bylong Valley has state heritage significance, as identified by the expert heritage report by Hector Abrahams Architects.
- The mine will irreparably damage these values, and also have broader heritage impacts because it adjoins the Greater Blue Mountains World Heritage Area.
- This mine will directly open cut strategic agricultural land which cannot be replaced. All such land should be off-limits to coal mining.
- The mine will destroy areas that have been mapped as part of the Critical Industry Cluster for the equine industry.
- This mine will devastate the Bylong River and its alluvial aquifer. Government experts warned internally the river could ‘run dry’ if the mine goes ahead.
In any case there should be no new coal mines. As explained in another article, the IPCC has released new warnings that global warming needs to be limited to 1.5°C and fossil fuels should be phased out quickly to avoid catastrophic change.
Oaks, Sheoaks and Medullary Rays
The names of many of our native trees were taken from perceived resemblances of their timbers to those of traditional Northern Hemisphere species like oak, and tropical hardwoods such as mahogany, something for which we can no doubt thank early settlers. On many occasions the common names mean little botanically but reflect species from unrelated plant families or with no close relatives among Australian flora. Let's take a classic example.
Red Cedar Toona ciliata is named after North American Western Red Cedar, or more correctly ‘Redcedar’ Thuja plicata of innumerable window frames and architraves. Our native version isn't even a conifer let alone a member of family Cupressaceae. T. ciliata, surprisingly, is actually in the Mahogany family Meliaceae and of course it's a hardwood.
From here we could move the article on to the various trees Australians call mahogany, with many examples, but what about our various ‘oaks’ such as Tasmanian ‘Tassie’ Oak, Silky Oak, Northern Silky Oak and the various ‘sheoaks’ ‘she oaks’ and ‘bull oaks’.
The term ‘Tassie oak’ generally embraces three species of Eucalyptus – E. regnans, E. obliqua and E. delegatensis all of which have hard, light coloured timbers in shades within oak's range, though they rarely show the classic feature of true Northern Hemisphere oak of the genus Quercus – that of medullary rays.
If you are unsure what a medullary ray is have a look at any oak furniture you may have. Or failing that, next time you are on a bushwalk and a Black Sheoak or Forest Oak has been blown down across a trail (a common event) and sawn up, look closely at the cut ends. The picture below is of just such a tree and you can clearly see striking, curvilinear radial streaks that cut across the concentric growth ring pattern. For the living tree these carried out a function of conducting water across the grain, but they also mature to an attractive and sought after feature of polished timber in cabinet making and wood turning.
As well as in members of family Casuarinaceae, medullary rays are typically also found in Proteaceae species, notably of course Silky Oak Grevillea robusta and Northern Silky Oak Cardwellia sublimis. We are perhaps lucky that the numerous beautiful plants of this family do not generally grow to timber size except to provide an occasional rare source for specialist ornate inlays and veneers.
You may own items of true oak furniture, or you may visit a pub, restaurant or antique shop or watch Antiques Roadshow, featuring traditional-style oak furniture, and see the rays expressed as graceful, wavy, lenticular patterns. But our very own silky oaks and sheoaks show these beautifully and have also been widely used historically, turning up in such settings as traditional church pews and well-crafted furniture and inlays. And although darker than real oak, you'll spot them immediately from their medullary flecks and patterns.
Alternative insight into the naming of tree species by John Martyn
2018 Young Scientist Award
STEP has been giving a Young Scientist prize at the annual awards every year since 2001. During this period the event has grown and grown, now with prizes totaling more than $30,000.00. All school years are covered, from K to year 12, and it was delightful to see some of the younger winners bouncing up onto the stage, and to learn how serious their projects were.
One highlight for us was the ongoing success of past two-times STEP winner Jade Moxey, now a Young Scientist ‘insider’ and a member of the stage party this year. She's also now a first year science student at Canberra Uni.
STEP gets to judge a selection of the order of six to eight entries picked by the board from the environmental side of the science projects. These usually cover a range of topics, but plastic bags and plastic pollution figured prominently this year. There were also bushland related ones, which for the past two years have featured Lake Parramatta Reserve, that precious little surviving enclave of sandstone flora that just happens to have several schools nearby. This year these schools generated a project on cicadas and another based on Powerful Owl sightings.
While STEP naturally welcomes the bushland projects, neither of this year's entries was a leader and our judgment favoured a neat little one on microplastic pollution of beach sand by a year 6 student. She is Beatrix Farley, from Castle Cove Public School, and the systematic nature of her collecting and observations, taken from beaches south of Sydney to as far north as Cape York Peninsula, plus her excellent presentation, won the day. Her results were to some degree counterintuitive too, the most polluted sands being collected from remote Cape York beaches, in her view related to the impact on that coastline of the South Equatorial Current. Her entry won her three other prizes and she was featured on stage as one of a small group of ‘primary scientists’.
There were, I feel, some minor downsides affecting our entries. Some written presentations were below par in being too long-winded, convoluted and slow to get to the point. One of the bushland related entries was peppered with spelling mistakes that could have easily been corrected by any spell checker. Such flaws will naturally cast a shadow over an otherwise well thought out project.
More...
Threatened Species Children’s Art Competition
This year 2749 children participated in the Children’s Threatened Species Art Competition. There were 2397 entries and over 100 schools and programs got involved. The organisers were delighted by the quality of the children's work, their concern for our threatened species, and their desire to make a difference.
The student's challenge is to research and create an artwork on one of the over 1000 threatened species in NSW and the ACT. The finalists’ works can be viewed on Facebook.
The image above expresses the encroaching development on the natural world says it so well for the regent honeyeater. Oscar 11 says:
I was inspired to paint the Regent Honeyeater because I like its bright yellow colours. I have painted it on the last tree in the city. The Regent Honeyeater has been badly affected by land-clearing and is endangered in NSW. At my school we have planted trees for habitat for native small birds.
I noticed that many schools are taking steps like this one to protect habitat for native species. Well done brilliant children and their teachers!
Annual Report for the Year to 30 June 2018
In 2018 STEP celebrated our 40th year of activity with a party at Lane Cove National Park and the publication of a history book written by Graeme Aplin. It was a delightful occasion catching up with several longstanding members such as past presidents Helen Petersen, Yvonne Langshaw, John Burke, Bruno Krockenberger and Barry Tomkinson.
At last year’s AGM an updated version of our constitution was approved. Basically our objectives remain unchanged but have been broadened to acknowledge that we cover more that the Ku-ring-gai area. In brief our objectives are to work for the conservation and proper management of bushland in northern Sydney, to promote participation of members via walks and talks and to promote environmental education.
This annual report gives a brief summary of our activities over the past year.
Committee
With so much development happening in Sydney and other threats to the environment throughout the state of NSW it has been another busy year for the committee in preparing submissions. We have also been very active in our other fields such as education and local walks with some other initiatives described in this report.
I pay tribute to the work of STEP’s committee members who are always willing to take the time to respond to issues as they arise and to implement new ideas.
I also thank some other individuals who have helped with our work, in particular Beverley Gwatkin for her organisation and communication skills, Peter Clarke for leading walks and Gaye Braiding for helping judge the Young Scientist Award.
Individuals who can offer their expertise and time to help with some aspect of our work are very welcome to let us know by contacting a member of the committee.
Publications
This year John Martyn has completed another book, called Rocks and Trees. It is beautiful photographic journey through the rich and varied geology, scenery and flora of the Sydney region. It has been well received in all areas where John has had the opportunity to demonstrate the book.
Our other publications continue to sell well.
Accounts
Our operations incurred a small deficit over the year but we remain in a sound financial position. Membership has remained steady.
We appreciate the pro bono work done by Allan Donald, Chartered Accountant, who completed the audit of STEP’s financial statements.
Environment Protection Fund
We have maintained the Environment Protection Fund which provides deductible gift recipient status for donations that support STEP’s environmental objectives. We received a total of $65 in donations in the past financial year.
We decided this year to direct some of the fund’s assets towards an annual grant to support student research in an area relating to the conservation of bushland. The inaugural John Martyn Research Grant was awarded to a PhD student studying the adaptive capacity of various acacia species to climate change.
Electronic Media
Helen Wortham has continued her brilliant job of keeping the website up-to-date and functioning as well as managing the email system by sending regular updates to members and compilation of the newsletter email and web page. The newsletter is now in an attractive and easy to use format so that individual stories can be selected or the whole newsletter can be downloaded.
Trish Lynch and John Burke continue to alert readers to current issues and events through Facebook and Twitter.
Education
We support the Young Scientist Awards run by the NSW Science Teachers’ Association with a prize in the environmental sustainability category. The winner of the STEP prize this year studied the levels of microplastics on Australian beaches.
We also supported the Children’s Threatened Species Art Competition. The primary school children produced some fabulous paintings that can be seen on the competition’s Facebook page.
Talks
Our talks covered a wide range of topics in terms of the subjects and time scale. They included topics of Sydney’s urban ecology, threatened species in Ku-ring-gai, and the Great Extinction event 252 million years ago. Teresa James helped launch John Martyn’s book with a talk on the plant communities of the Sydney Basin.
Walks
Several of our walks also had a geological focus at Long Reef and Munmorah plus we explored the wildflowers in local national parks and organised a guided Aboriginal Heritage walk.
We also started a series of local walks to be held every couple of months aimed at introducing the public to the experience our local bushland. We thank John Martyn and Peter Clarke for organising and leading walks this past year. If you have a request for a walk please let us know.
Newsletter
Our newsletter, STEP Matters, is our main means of communicating events, our activities and current issues. We also include other articles with an environmental angle that will be of interest to members. The newsletter is also sent to local councillors and politicians. We welcome alerts from our members of local events and developments and, of course, feedback on articles is always welcome.
Powerful Owl Coalition
In response to the continuing adverse impacts on our native wildlife and their habitat STEP has joined with other local groups to establish the Powerful Owl Coalition. We have produced a brochure for the general public and a detailed position paper aimed at educating various professions and agencies whose work and policies impact on Powerful Owl habitat on how to enhance this habitat. Of course the preservation of this habitat happens to be a core objective of STEP’s work. We hope to expand the coalition to include community groups in all areas where the owls live.
Advocacy
The main local issues of concern that have occupied our attention have been the night lighting of the Canoon Road netball courts, illegal mountain bike activity and the Mirvac development proposals next to Cumberland State Forest in West Pennant Hills.
At the state level the government continues their poor environment record with more decisions such as protection of feral horses in Koscuiszko National Park and potential flooding of the World Heritage Blue Mountains by raising the Warragamba Dam wall. This is on top of the habitat loss from the relaxation of land clearing laws that is now starting to become apparent.
New Walk Series – Introduction to our Local Bushland
STEP member, Beverley Gwatkin, came up with the great idea of conducting walks for people unfamiliar with the amazing features of our local bushland so she approached Peter Clarke who agreed to lead the walks.
Until his recent retirement, Peter was Ku-ring-gai Council’s community volunteer program coordinator, so he has a wealth of knowledge about the local flora and fauna.
STEP will be organising a walk every couple of months on a Sunday morning. Click here for more information and to register.
Guided Aboriginal Heritage Walk around North Head
 This walk on 22 June was fascinating. We heard all about the diverse diet and life of the local Kai’ymay clan, the history of encounters between the aboriginal people and colonialists. The two hour walk ended up going on for four hours!
This walk on 22 June was fascinating. We heard all about the diverse diet and life of the local Kai’ymay clan, the history of encounters between the aboriginal people and colonialists. The two hour walk ended up going on for four hours!
Did you know that the first known map of Port Jackson had the name of Eve’s Cove for the area now known as Manly Cove? The area was given this name after the first meeting of the British settlers and some aboriginal women on 29 January 1788.
The walk was led by Karen Smith from the Aboriginal Heritage Office. The office’s main role is to regularly monitor and manage Aboriginal heritage sites to ensure their protection. The Aboriginal Heritage Office develops and implements community education programs and events aimed at increasing the collective knowledge of Aboriginal cultural heritage.