Displaying items by tag: marine parks
Hopes for Marine National Parks Protection Slashed
It has been a long drawn out process to develop a National Representative System of Marine Protected Areas (NRSMPA). In 1998 the commonwealth, states and Northern Territory governments committed themselves to establishing the NRSMPA by 2012. The Australian government affirmed this commitment at the United Nations World Summit on Sustainable Development in 2002.
The states are responsible for managing coastal waters out to 3 nautical miles offshore. Beyond that marine management is the Australian government’s responsibility.
The primary goal of the NRSMPA is to establish and effectively manage a comprehensive, adequate and representative system of marine reserves to contribute to the long-term conservation of marine ecosystems and to protect marine biodiversity.
After extensive consultation and scientific analysis the Gillard government declared a new network of marine reserves and plans of management that took effect in November 2012. The reserves cover 36% of Commonwealth waters with various levels of protection.
At the time there were protests from fishing industries but it was estimated by the Australian Bureau of Agricultural and Resource Economics and Sciences that only around 1% of the total annual value of Australia's commercial fisheries would be displaced.
The Abbott government came into power in September 2013 and in December suspended the declarations and management plans for these new reserves and instituted another review claiming that the science in the previous review was inadequate.
Draft revised plans from this review was released in 2017 and in March 2018 the final decision was announced by Environment Minister Frydenberg.
All the fears of the marine scientists that the science would be ignored have been realised. The draft proposals are to be implemented despite the protests exemplified by the statement below.
Government Decision
The government claims that the amended policy is a balanced and scientific evidence-based approach to ocean protection. However the marine conservation groups, such as Save Our Marine Life and WWF, have condemned the reductions in protection levels. In their view a particularly insidious form of partial protection is that of ‘habitat protection zones’ whereby only activities that affect the seabed are excluded. Such zoning ignores the important biological links between animals in the water column and the seabed. It allows commercial fishing activities within the marine parks that have already been assessed as incompatible with conservation in the government’s own risk reports. Indeed, such zoning creates the opportunity for industrial scale fishing within our marine parks by vessels such as the imported Dutch super trawler, the Geelong Star, that so many Australians rejected.
Sadly the Senate passed the new management plans on 27 March. Labor and the Greens could not marshal enough support from the independents to oppose the plans.
The following is a statement from the Ocean Science Council of Australia, an internationally recognised independent group of university-based Australian marine researchers, and signed by 1,286 researchers from 45 countries and jurisdictions, in response to the federal government’s draft marine parks plans.
We, the undersigned scientists, are deeply concerned about the future of the Australian Marine Parks Network and the apparent abandoning of science-based policy by the Australian government.
On 21 July 2017, the Australian government released draft management plans that recommend how the Marine Parks Network should be managed. These plans are deeply flawed from a science perspective.
Of particular concern to scientists is the government’s proposal to significantly reduce high-level or 'no-take' protection (Marine National Park Zone IUCN II), replacing it with partial protection (Habitat Protection Zone IUCN IV), the benefits of which are at best modest but more generally have been shown to be inadequate.
The 2012 expansion of Australia’s Marine Parks Network was a major step forward in the conservation of marine biodiversity, providing protection to habitats and ecological processes critical to marine life. However, there were flaws in the location of the parks and their planned protection levels, with barely 3% of the continental shelf, the area subject to greatest human use, afforded high-level protection status, and most of that of residual importance to biodiversity.
The government’s 2013 Review of the Australian Marine Parks Network had the potential to address these flaws and strengthen protection. However, the draft management plans have proposed severe reductions in high-level protection of almost 400,000 square kilometres – that is, 46% of the high-level protection in the marine parks established in 2012.
Commercial fishing would be allowed in 80% of the waters within the marine parks, including activities assessed by the government’s own risk assessments as incompatible with conservation. Recreational fishing would occur in 97% of Commonwealth waters up to 100km from the coast, ignoring the evidence documenting the negative impacts of recreational fishing on biodiversity outcomes.
Under the draft plans:
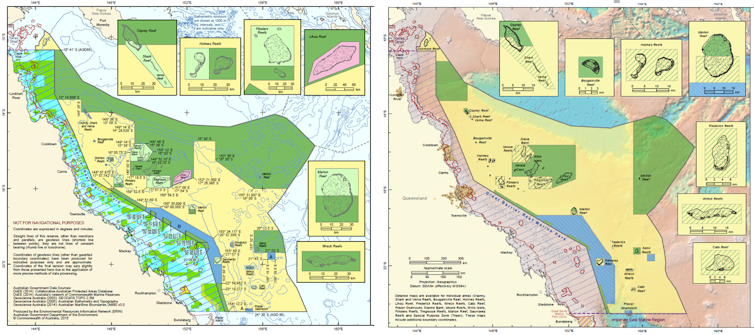
the Coral Sea Marine Park, which links the iconic Great Barrier Reef Marine Park to the waters of New Caledonia’s Exclusive Economic Zone (also under consideration for protection), has had its Marine National Park Zones (IUCN II) reduced in area by approximately 53% (see map below)
six of the largest marine parks have had the area of their Marine National Park Zones IUCN II reduced by between 42% and 73%
two marine parks have been entirely stripped of any high-level protection, leaving 16 of the 44 marine parks created in 2012 without any form of Marine National Park IUCN II protection
Proposed Coral Sea Marine Park zoning, as recommended by independent review (left) and in the new draft plan (right), showing the proposed expansion of partial protection (yellow) vs full protection (green). From http://www.environment.gov.au/marinereservesreview/reports and https://parksaustralia.gov.au/marine/management/draft-plans
The replacement of high-level protection with partial protection is not supported by science. The government’s own economic analyses also indicate that such a reduction in protection offers little more than marginal economic benefits to a very small number of commercial fishery licence-holders.
Retrograde step
This retrograde step by Australia’s government is a matter of both national and international significance. Australia has been a world leader in marine conservation for decades, beginning with the establishment of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in the 1970s and its expanded protection in 2004.
At a time when oceans are under increasing pressure from overexploitation, climate change, industrialisation, and plastics and other forms of pollution, building resilience through highly protected Marine National Park IUCN II Zones is well supported by decades of science. This research documents how high-level protection conserves biodiversity, enhances fisheries and assists ecosystem recovery, serving as essential reference areas against which areas that are subject to human activity can be compared to assess impact.
The establishment of a strong backbone of high-level protection within Marine National Park Zones throughout Australia’s Exclusive Economic Zone would be a scientifically based contribution to the protection of intact marine ecosystems globally. Such protection is consistent with the move by many countries, including Chile, France, Kiribati, New Zealand, Russia, the UK and US to establish very large no-take marine reserves. In stark contrast, the implementation of the government’s draft management plans would see Australia become the first nation to retreat on ocean protection.
Australia’s oceans are a global asset, spanning tropical, temperate and Antarctic waters. They support six of the seven known species of marine turtles and more than half of the world’s whale and dolphin species. Australia’s oceans are home to more than 20% of the world’s fish species and are a hotspot of marine endemism. By properly protecting them, Australia will be supporting the maintenance of our global ocean heritage.
The finalisation of the Marine Parks Network remains a remarkable opportunity for the Australian government to strengthen the levels of Marine National Park Zone IUCN II protection and to do so on the back of strong evidence. In contrast, implementation of the government’s retrograde draft management plans undermines ocean resilience and would allow damaging activities to proceed in the absence of proof of impact, ignoring the fact that a lack of evidence does not mean a lack of impact. These draft plans deny the science-based evidence.
We encourage the Australian government to increase the number and area of Marine National Park IUCN II Zones, building on the large body of science that supports such decision-making. This means achieving a target of at least 30% of each marine habitat in these zones, which is supported by Australian and international marine scientists and affirmed by the 2014 World Parks Congress in Sydney and the IUCN Members Assembly at the 2016 World Conservation Congress in Hawaii.
![]() You can read a fully referenced version of the science statement here, and see the list of signatories here.
You can read a fully referenced version of the science statement here, and see the list of signatories here.
Jessica Meeuwig, Professor and Director, Marine Futures Lab, University of Western Australia
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
Why are Australia's Marine Parks being Reviewed so Soon after they were Signed Off?
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.